Diagram of Urinary System
Last Updated : 15 Apr, 2025
The diagram of urinary system shows the organs responsible for producing, storing, and excreting urine from the body. The diagram of the urinary system of humans shows that it is made of kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. It also includes additional structures like renal arteries and veins, which supply blood to the kidneys and adrenal glands.
Understanding the urinary system diagram is important for health professionals and students alike. Diagrams of the urinary system in classes 7 and 10 are often asked in the examinations. You can find the labeled urinary system diagram in this article.
What is Urinary System?
The urinary system is also known as the renal system or urinary tract. The diagram of urinary system shows that it is made of - kidneys, ureters, the bladder, and the urethra. The primary function of the urinary system is to eliminate waste from the body and regulate blood volume and pressure, maintain blood pH balance, and control metabolite levels. It serves as the body's drainage system, and removes waste through urine.
Also read: Human urinary system
Diagram of Urinary System
The urinary system diagram with labelling is given below:
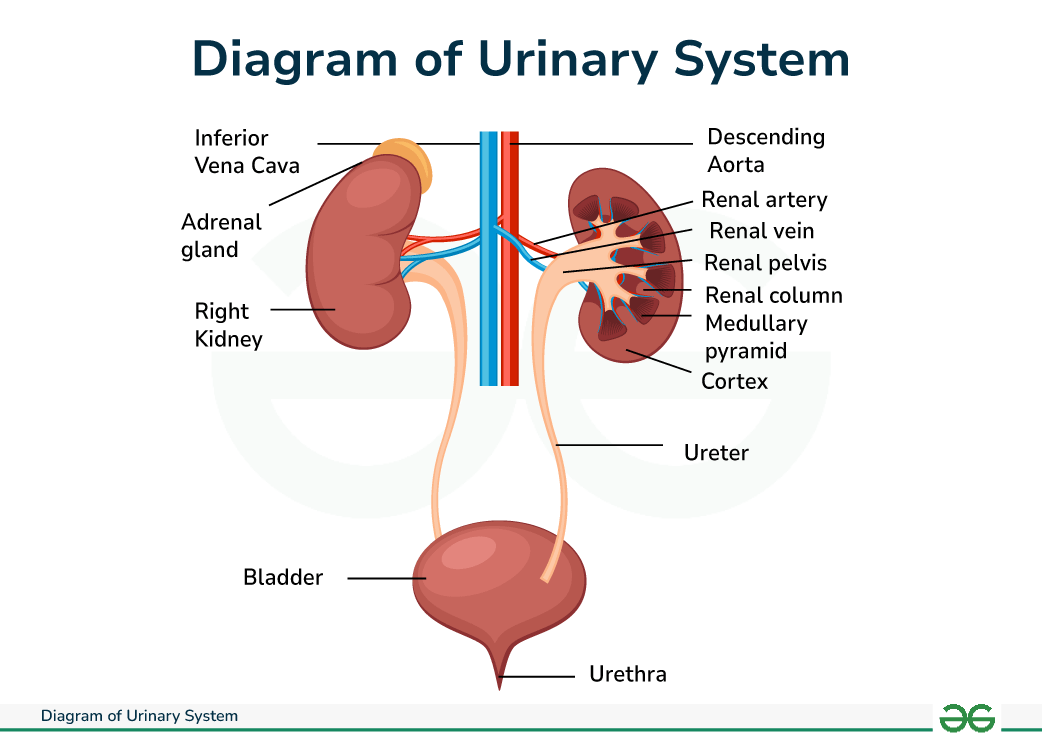 Urinary System Diagram
Urinary System DiagramStructure of Urinary System
The various organs of urinary system are mentioned here along with their functions:
Kidney
The kidney are two-bean shaped organs one on either side of the spine.They produce 1 to 2 quarts of urine daily. Each kidney is shielded and surrounded by three layers of tissue:
- Renal capsule: This is the innermost layer consisting of a smooth fibrous membrane
- Adipose capsule: A layer composed of fatty tissue
- Renal fascia: the outermost layer comprising of connective tissue that anchors the kidney to the abdominal wall.
The kidneys outer region is called cortex, while the medulla is situated at its center. Within the medulla are 10-15 cone shaped collecting ducts known as renal pyramids. These ducts drain into the minor calyces (which are cup-shaped receptacles). From there, the urine flows into the major calyces, larger openings leading to the renal pelvis, which is funnel shaped. Ultimately, urine travels through the ureter to the bladder.
Ureters
The ureters, thin hollow tube, emerge from each kidney and extend into the urinary bladder.
- They enter the bladder walls from either side forming a U - shape. At the bottom of this U shape, the ureter connects to the triangular area on the base of the bladder called the trigone.
- As the kidney converts waste into urine, muscles lining the walls of the ureters help propel the urine towards the bladder for storage.
- The urine enters the bladder through the ureteral openings. The mucous membrane lining the ureters stores urine in the bladder and prevent it from refluxing back towards the kidney, which could lead to infection.
Bladder
The bladder, muscular hollow organ, serves as a reservoir for the urine until it is expelled from the body. Positioned in the abdomen behind the pubic bone, it contains an opening to the urethra at the base of the trigone, through which urine exist the body. Internally, the bladder consist of three layers:
- Serosa: The outer coat providing protective covering.
- Detrusor muscle: a collective term for three layer of smooth muscle responsible for bladder contraction and relaxation.
- Mucosa: The innermost layer lining the bladder.
Prostrate gland
In males, the prostrate gland which encircles the junction where the bladder connects resembling a doughnut shape.
- In young man, the prostrate gland is typically size and shape of walnut. However, it enlarges with age.
- The primary function of the prostrate gland is to contribute fluid volume and essential nutrients to semen.
- Within the prostrate gland, numerous tiny glands produce fluid that merges with the sperm in the urethra during orgasm. This combined mixture is expelled during ejaculation.
Urethra
The urethra is a muscular tube that links the bladder to the exterior providing a passage for urine to be expelled from the body.
- Its structure includes a mucous membrane and a layer of smooth muscle tissue. Notably, there are distinctions in the function, trajectory and length of the urethra between males and females.
- In males the urethra extends by 8 inches connecting bladder to the tip of the penis. Whereas, in females, the urethra measures approximately 1.5 inches in length, which contributes to their increased susceptibility to urinary tract infection.
- The shorter length facilitates the movement of urine back to the bladder, increasing the risk of infection.
Urinary sphincter muscle
Sphincter consist of two types of muscles responsible for controlling flow of urine from the bladder.
- At the junction of the urethra and bladder, internal urethral sphincter, comprising involuntary muscle, prevent urine from refluxing back into the bladder.
- External urethral sphincter, located at the end of the urethra, are voluntary muscles that initiate and cease the flow of urine by relaxing and contracting.
- Both set of sphincter muscle facilitates the movement of urine out of the body when they are open, and they prevent urine from escaping when closed. These muscles work in the coordination with the bladder: when the bladder relaxes to allow urine to enter, the sphincter muscles remain closed to prevent leakage.
- During urination, when the bladder contracts, the sphincter muscle relaxesmallowing urine to flow out of the body.
Urinary System Diagram with Functions
The urinary system diagram given above clearly shows the detailed parts of the human urinary system. Now, let us discuss its functions in brief:
- Waste Removal: Filters and removes waste products and excess substances from the blood by forming urine.
- Fluid Balance: Regulates the volume of body fluids by adjusting the amount of water excreted.
- Electrolyte Balance: Urinary system maintains the balance of electrolytes (such as sodium, potassium, and calcium) in the body.
- Blood Pressure Regulation: Helps control blood pressure by adjusting the volume of blood and releasing the enzyme renin.
- pH Balance: Maintains the acid-base balance of the blood by excreting hydrogen ions and reabsorbing bicarbonate.
- Red Blood Cell Production: Produces the hormone erythropoietin, which stimulates red blood cell production in the bone marrow.
- Detoxification: Urinary system helps in detoxifying certain drugs and chemicals from the bloodstream.
Conclusion - Diagram of Urinary System
The urinary system is important for maintaining the body's internal balance by regulating fluid levels, electrolytes and eliminating waste products. The diagram of urinary system shows that it is comprised of organs like the kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra. The kidneys filter blood, removing waste and excess substance to produce urine, which travels through the ureters to the bladder for storage. Controlled by sphincter muscles, urine is expelled through the urethra during urination. The proper function of this system is fundamental to overall heath, as disruption may lead to complications such as kidney stones or urinary tract infections.
Other Diagram Related Article Links
Also Read: