Design counter for given sequence
Last Updated : 13 Sep, 2024
A Counter is a device which stores (and sometimes displays) the number of times a particular event or process has occurred, often in relationship to a clock signal. Counters are used in digital electronics for counting purpose, they can count specific event happening in the circuit. For example, in UP counter a counter increases count for every rising edge of clock.
What is Counter?
Counter is a sequential circuit implemented via flip flops. They are used to count the number of clock signals or pulse. A mod n counter will count from 0 to n-1.
Counters can be synchronous or unsynchronous. In synchronous counter, a single common clock is used for all the flip flops. Whereas in asynchronous counter, only a clock is given as input for first flip flop. For an intermediate or final flip flops, its clock pulse will be the output of previous flip flop.
Problem - Design synchronous counter for sequence: 0 → 1 → 3 → 4 → 5 → 7 → 0, using T flip-flop. Explanation - For given sequence, state transition diagram as following below:  State transition Table logic
State transition Table logic
| Present State | Next State |
|---|
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 3 |
| 3 | 4 |
| 4 | 5 |
| 5 | 7 |
| 7 | 0 |
State transition table for given sequence
| Present State | Next State |
|---|
| Q3 | Q2 | Q1 | Q3(t+1) | Q2(t+1) | Q1(t+1) |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
T flip-flop - If value of Q changes either from 0 to 1 or from 1 to 0 then input for T flip-flop is 1 else input value is 0.
Draw input table of all T flip-flops by using the excitation table of T flip-flop. As nature of T flip-flop is toggle in nature. Here, Q3 as Most significant bit and Q1 as least significant bit.
| Input table of Flip-Flops |
|---|
| T3 | T2 | T1 | |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | |
Find value of T3, T2, T1 in terms of Q3, Q2, Q1 using K-Map (Karnaugh Map):  Therefore,
Therefore,
T3 = Q2
 Therefore,
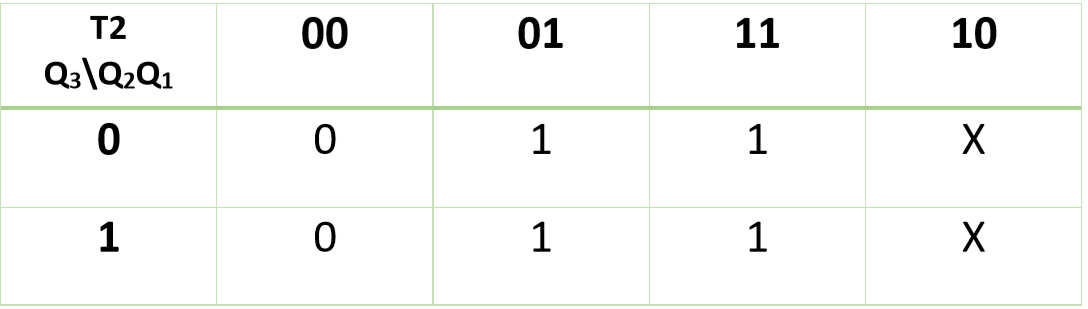
Therefore,
T2 = Q1
.webp) K map
K map
Therefore,
T1 = Q2+Q1'
Now, you can design required circuit using expressions of K-maps: 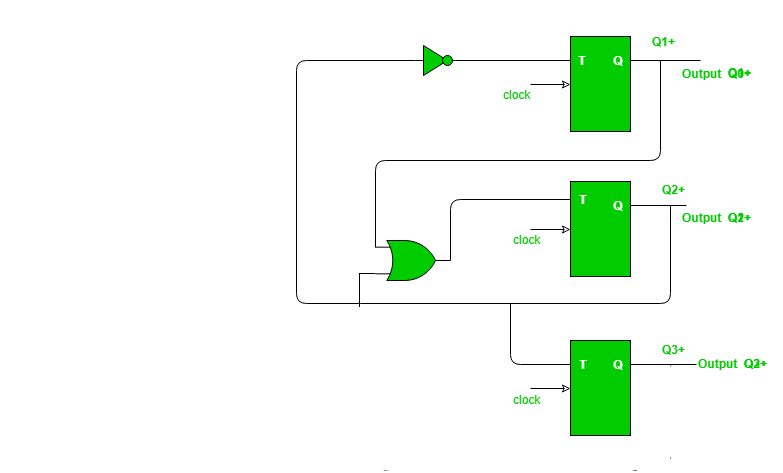
Advantages of Counters
- Counters can be use for measuring time. E.g. Elapsed time, Response time, etc.
- They can be used in real time system
- They are easy to implement and cost effective
Disadvantages of Counters
- The hazards and delay in flip-flop can create error
- Different digital circuit are to be realized for different value of n and type of flip flop used in n-mod counter
Conclusion
To design a counter for given sequence, we must first design the state transition diagram and table. And then we have to chose the type and number of flip flops. We have to find the excitation table for the same. And we have to simply the equation using K-map or Quine McCluskey (tabular) Method.
Similar Reads
Parallel Adder and Parallel Subtractor An adder adds two binary numbers one bit at a time using carry from each step. A subtractor subtracts one binary number from another using borrow when needed. A parallel adder adds all bits at once, making addition faster. Similarly, a parallel subtractor subtracts all bits at the same time for quic
5 min read
BCD Adder in Digital Logic BCD stands for binary coded decimal. It is used to perform the addition of BCD numbers. A BCD digit can have any of ten possible four-bit representations. Suppose, we have two 4-bit numbers A and B. The value of A and B can vary from 0(0000 in binary) to 9(1001 in binary) because we are considering
8 min read
Magnitude Comparator in Digital Logic A magnitude digital Comparator is a combinational circuit that compares two digital or binary numbers in order to find out whether one binary number is equal, less than, or greater than the other binary number. We logically design a circuit for which we will have two inputs one for A and the other f
7 min read
BCD to 7 Segment Decoder Prerequisite - Number System and base conversionsBinary Coded Decimal (BCD)BCD is the encoding scheme each of the decimal numbers(0-9) is represented by its equivalent binary pattern(which is generally of 4-bits). Seven segment Seven Segment display is an electronic device which consists of seven Li
5 min read
Classification and Programming of Read-Only Memory (ROM) Read-Only Memory or ROM is another significant non Volatile storage control in computed systems which mainly stores data permanently whether the power is off or not. While RAM is a temporary storage type used in computers and printers, ROM contains firmware and other instructions which are burnt, in
15+ min read
Static Hazards in Digital Logic A hazard, if exists, in a digital circuit causes a temporary fluctuation in the output of the circuit. In other words, a hazard in a digital circuit is a temporary disturbance in the ideal operation of the circuit which if given some time, gets resolved itself. These disturbances or fluctuations occ
4 min read
Introduction of Sequential Circuits Sequential circuits are digital circuits that store and use the previous state information to determine their next state. Unlike combinational circuits, which only depend on the current input values to produce outputs, sequential circuits depend on both the current inputs and the previous state stor
7 min read
Flip-Flop types, their Conversion and Applications In this article, we will go through the Flip-Flop types, their Conversion and their Applications, First, we will go through the definition of the flip-flop with its types in brief, and then we will go through the conversion of the flip-flop with its applications, At last, we will conclude our articl
7 min read
Synchronous Sequential Circuits in Digital Logic Synchronous sequential circuits are digital circuits that use clock signals to determine the timing of their operations. They are commonly used in digital systems to implement timers, counters, and memory elements.What is Sequential Circuit?A sequential circuit is a digital circuit, whose output dep
5 min read
Counters in Digital Logic A Counter is a device which stores (and sometimes displays) the number of times a particular event or process has occurred, often in relationship to a clock signal. Counters are used in digital electronics for counting purpose, they can count specific event happening in the circuit. For example, in
4 min read