Data Communication - Definition, Components, Types, Channels
Last Updated : 19 Dec, 2024
Transferring data over a transmission medium between two or more devices, systems, or places is known as data communication. Nowadays, computing and telecommunications depend heavily on this data transmission, which makes a variety of applications conceivable, including email, video chatting, the Internet, and many more things.
In this article, we will learn about Data communication, Definition, Components, Types, and Channels.
Components of Data Communication
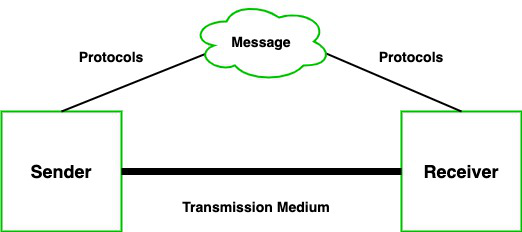
A communication system is made up of the following components:
- Message: A message is a piece of information that is to be transmitted from one person to another. It could be a text file, an audio file, a video file, etc.
- Sender: It is simply a device that sends data messages. It can be a computer, mobile, telephone, laptop, video camera, or workstation, etc.
- Receiver: It is a device that receives messages. It can be a computer, telephone mobile, workstation, etc.
- Transmission Medium / Communication Channels: Communication channels are the medium that connect two or more workstations. Workstations can be connected by either wired media or wireless media.
- Set of rules (Protocol): When someone sends the data (The sender), it should be understandable to the receiver also otherwise it is meaningless. For example, Sonali sends a message to Chetan. If Sonali writes in Hindi and Chetan cannot understand Hindi, it is a meaningless conversation.
Therefore, there are some set of rules (protocols) that is followed by every computer connected to the internet and they are:
- TCP(Transmission Control Protocol): It is responsible for dividing messages into packets on the source computer and reassembling the received packet at the destination or recipient computer. It also makes sure that the packets have the information about the source of the message data, the destination of the message data, the sequence in which the message data should be re-assembled, and checks if the message has been sent correctly to the specific destination.
- IP(Internet Protocol): Do You ever wonder how computer determines which packet belongs to which device. What happens if the message you sent to your friend is received by your father? Scary Right. Well! IP is responsible for handling the address of the destination computer so that each packet is sent to its proper destination.
Type of data communication
As we know that data communication is communication in which we can send or receive data from one device to another. The data communication is divided into three types:
- Simplex Communication: It is one-way communication or we can say that unidirectional communication in which one device only receives and another device only sends data and devices uses their entire capacity in transmission. For example, IoT, entering data using a keyboard, listening music using a speaker, etc.
- Half Duplex communication: It is a two-way communication, or we can say that it is a bidirectional communication in which both the devices can send and receive data but not at the same time. When one device is sending data then another device is only receiving and vice-versa. For example, walkie-talkie.
- Full-duplex communication: It is a two-way communication or we can say that it is a bidirectional communication in which both the devices can send and receive data at the same time. For example, mobile phones, landlines, etc.
Communication Channels
Communication channels are the medium that connects two or more workstations. Workstations can be connected by either wired media or wireless media. It is also known as a transmission medium. The transmission medium or channel is a link that carries messages between two or more devices. We can group the communication media into two categories:
- Guided media transmission
- Unguided media transmission
1. Guided Media: In this transmission medium, the physical link is created using wires or cables between two or more computers or devices, and then the data is transmitted using these cables in terms of signals. Guided media transmission of the following types:
1. Twisted pair cable: It is the most common form of wire used in communication. In a twisted-pair cable, two identical wires are wrapped together in a double helix. The twisting of the wire reduces the crosstalk. It is known as the leaking of a signal from one wire to another due to which signal can corrupt and can cause network errors. The twisting protects the wire from internal crosstalk as well as external forms of signal interference. Types of Twisted Pair Cable :
- Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP): It is used in computers and telephones widely. As the name suggests, there is no external shielding so it does not protects from external interference. It is cheaper than STP.
- Shielded Twisted Pair (STP): It offers greater protection from crosstalk due to shield. Due to shielding, it protects from external interference. It is heavier and costlier as compare to UTP.
2. Coaxial Cable: It consists of a solid wire core that is surrounded by one or more foil or wire shields. The inner core of the coaxial cable carries the signal and the outer shield provides the ground. It is widely used for television signals and also used by large corporations in building security systems. Data transmission of this cable is better but expensive as compared to twisted pair.
3. Optical fibers: Optical fiber is an important technology. It transmits large amounts of data at very high speeds due to which it is widely used in internet cables. It carries data as a light that travels inside a thin glass fiber. The fiber optic cable is made up of three pieces:
- Core: Core is the piece through which light travels. It is generally created using glass or plastic.
- Cladding: It is the covering of the core and reflects the light back to the core.
- Sheath: It is the protective covering that protects fiber cable from the environment.
2. Unguided Media: The unguided transmission media is a transmission mode in which the signals are propagated from one device to another device wirelessly. Signals can wave through the air, water, or vacuum. It is generally used to transmit signals in all directions. Unguided Media is further divided into various parts :
1. Microwave: Microwave offers communication without the use of cables. Microwave signals are just like radio and television signals. It is used in long-distance communication. Microwave transmission consists of a transmitter, receiver, and atmosphere. In microwave communication, there are parabolic antennas that are mounted on the towers to send a beam to another antenna. The higher the tower, the greater the range.
2. Radio wave: When communication is carried out by radio frequencies, then it is termed radio waves transmission. It offers mobility. It is consists of the transmitter and the receiver. Both use antennas to radiate and capture the radio signal.
3. Infrared: It is short-distance communication and can pass through any object. It is generally used in TV remotes, wireless mouse, etc.
Conclusion of Data Communication
A key component of modern technology, data transmission reduces the flow of information between networks, systems, and devices. To guarantee that data is sent exactly, quickly, and securely, it uses a variety of techniques and protocols.
Similar Reads
Data Communication Tutorial Data communication plays an important role in today's interconnected world and enables the exchange of information between devices and networks. Whether you're sending an email, making a video call, or browsing the web, data communication ensures that information flows smoothly. This Data Communicat
5 min read
Basics of Data Communication
Data Communication - Definition, Components, Types, ChannelsTransferring data over a transmission medium between two or more devices, systems, or places is known as data communication. Nowadays, computing and telecommunications depend heavily on this data transmission, which makes a variety of applications conceivable, including email, video chatting, the In
7 min read
Types of Computer NetworksA computer network is a system that connects many independent computers to share information (data) and resources. The integration of computers and other different devices allows users to communicate more easily. It is a collection of two or more computer systems that are linked together. A network
11 min read
Transmission Modes in Computer Networks (Simplex, Half-Duplex and Full-Duplex)Transmission modes also known as communication modes, are methods of transferring data between devices on buses and networks designed to facilitate communication. They are classified into three types: Simplex Mode, Half-Duplex Mode, and Full-Duplex Mode. In this article, we will discuss Transmission
6 min read
Difference Between Serial and Parallel TransmissionData transmission is how computers and other devices send information to each other. There are two main ways to do this Serial and Parallel Transmission. In Serial Transmission, data is sent one bit at a time like sending a single line of people through a door. In Parallel Transmission data is sent
4 min read
How Data Encapsulation and De-encapsulation Works?Data encapsulation and de-encapsulation are fundamental concepts in computer networking and communication protocols. These processes are essential for transferring data across networks efficiently and securely. What is Data Encapsulation?Encapsulation is the process of adding additional information
4 min read
OSI Model
TCP/IP Model The TCP/IP model (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) is a four-layer networking framework that enables reliable communication between devices over interconnected networks. It provides a standardized set of protocols for transmitting data across interconnected networks, ensuring efficie
7 min read
Data and Signals
Transmission of Signals
Transmission Impairment in Data CommunicationIn communication system, analog signals travel through transmission media, which tends to deteriorate the quality of analog signal, which means that the signal at the beginning of the medium is not the same as the signal at the end of the medium. The imperfection causes signal impairment. Below are
3 min read
What is Bandwidth? Definition, Working, Importance, UsesPre-Requisite: Introduction to Bandwidth Network bandwidth is the maximum capacity of a wired or wireless communications link to deliver data via a network connection in a given amount of time. Bandwidth is typically defined as the number of bits, kilobits, megabits, or gigabits that may be sent in
8 min read
Digital To Digital Conversion in Computer NetworkIn this article we will be discussing about digital-to-digital transmission in computer network i.e., how a digital data or information is converted into digital signal. The digital-to-digital encoding can be done by a technique called line coding. Line CodingThe process of converting the digital da
5 min read
Line CodingThe process of converting binary data into a sequence of bits of the digital signal is known as Line coding. It is also known as digital PAM formats. Need of Line coding: We always come across different types of data such as text, numbers, graphical images, audio, and video. These all data are store
2 min read
Analog to Digital ConversionDigital Signal: A digital signal is a signal that represents data as a sequence of discrete values; at any given time it can only take on one of a finite number of values. Analog Signal: An analog signal is any continuous signal for which the time varying feature of the signal is a representation of
6 min read
Digital to Analog ConversionDigital Signal - A digital signal is a signal that represents data as a sequence of discrete values; at any given time it can only take on one of a finite number of values. Analog Signal - An analog signal is any continuous signal for which the time varying feature of the signal is a representation
3 min read
Quadrature Amplitude ModulationQuadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) is a modulation technique that can be utilized in Analog modulation concepts and digital modulation concepts. It is a combination of ASK and PSK. So, in this article, we will discuss QAM, Analog QAM, Digital QAM, and many more. Quadrature Amplitude Modulation:Qu
5 min read
Analog to Analog Conversion (Modulation)Analog Signal: An analog signal is any continuous signal for which the time varying feature of the signal is a representation of some other time varying quantity i.e., analogous to another time varying Signal. Analog to Analog Conversion - Analog-to-analog conversion, or modulation, is the represent
3 min read
What is Modulation?Modulation can be digital or analog, the input wave of the analog signal varies continuously like a sine wave. Modulation can be defined as the process of converting data into waves by adding information to a carrier signal. Such a signal can be transmitted electronically or optically, but it must h
6 min read
Multiplexing
Transmission Media
Types of Transmission MediaTransmission media is the physical medium through which data is transmitted from one device to another within a network. These media can be wired or wireless. The choice of medium depends on factors like distance, speed, and interference. In this article, we will discuss the transmission media. In t
9 min read
Twisted-pair CableTwisted-pair Cable is a transmission media. Transmission media refers to the physical path or medium used to transmit data between devices. It can be divided into two parts: Guided Media and Unguided Media. In guided media, the signal is contained within the physical limits of the transmission mediu
4 min read
What is Coaxial Cable ?Coaxial cable is typically used by cable operators, telephone companies, and internet providers to transmit data, video, and voice communications to customers. Its installation and implementation are easy but it is less efficient than optical fiber also it provides moderately low bandwidth in compar
6 min read
Fiber Optics and TypesFiber Optics or Optical Fiber is a technology that transmits data as a light pulse along a glass or plastic fiber. An Optical Fiber is a cylindrical fiber of glass that is hair-thin in size or any transparent dielectric medium. The fiber which is used for optical communication is waveguides made of
6 min read
Difference between Twisted pair cable, Co-axial cable and Optical fiber cableA computer cable is a medium used to transmit data between devices such as computers, servers, routers, and switches. Cables physically connect these devices, enabling them to communicate within a network. In computer networking, it is very important to know the distinctions between the different ty
8 min read
Radio WavesRadio waves are a special type of energy that travels through space, carrying information without needing wires. They have the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, meaning they stretch out much farther than other waves like visible light or X-rays. These waves can be incredibly long,
9 min read
Infrared light for TransmissionInfrared light for Transmission :Infrared is the frequency of light that is not visible to the eyes .The frequency of the waves lies between three hundred gigacycles to four hundred THz. In this, the radiation is in the region of the electromagnetic spectrum . Infrared could be a communication mediu
3 min read
Difference between Guided and Unguided MediaNetwork media or transmission media refer to the physical pathways through which data is transmitted from one device to another within a network. These ways can be wired or wireless. The selection of media depends on factors like distance, speed, and interference. In this article, we will discuss th
4 min read
Error Detection and Correction
Channelization