Difference Between IPv4 and IPv6
Last Updated : 27 Dec, 2024
In the digital world, where billions of devices connect and communicate, Internet Protocol (IP) Addresses play a crucial role. These addresses are what allow devices to identify and locate each other on a network.
To know all about IP Addresses - refer to What is an IP Address?
Currently, there are two primary versions of Internet Protocol in use: IPv4 and IPv6. Each version has distinct characteristics, capabilities, and was developed to meet the specific needs of the internet's growth. IPv4 was the first to be widely implemented, laying the groundwork for early network communications.
However, as the internet grew and more devices started connecting online, the limitations of IPv4 became clear, leading to the creation of IPv6. This newer version was designed to address the shortcomings of its predecessor and to future-proof the network against an ever-increasing demand for more addresses and improved network efficiency.
Let’s explore their differences, why both are still in use, and the advantages each offers.
What is IPv4?
IPv4, or Internet Protocol version 4, is the original addressing system of the Internet, introduced in 1983. It uses a 32-bit address scheme, which theoretically allows for over 4 billion unique addresses (2^32). IPv4 addresses are typically displayed in decimal format, divided into four octets separated by dots. For example, 192.168.1.1 is a common IPv4 address you might find in a home network.
IPv4 Address Format is a 32-bit Address that comprises binary digits separated by a dot (.).
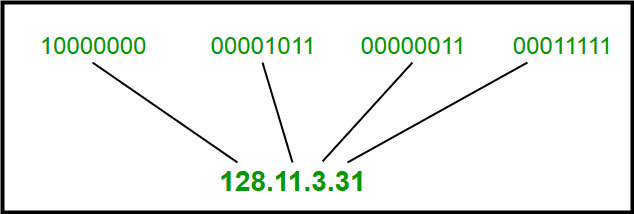 IPv4 Address Format
IPv4 Address FormatCharacteristics of IPv4
- 32-bit address length: Allows for approximately 4.3 billion unique addresses.
- Dot-decimal notation: IP addresses are written in a format of four decimal numbers separated by dots, such as 192.168.1.1.
- Packet structure: Includes a header and payload; the header contains information essential for routing and delivery.
- Checksum fields: Uses checksums in the header for error-checking the header integrity.
- Fragmentation: Allows packets to be fragmented at routers along the route if the packet size exceeds the maximum transmission unit (MTU).
- Address Resolution Protocol (ARP): Used for mapping IP network addresses to the hardware addresses used by a data link protocol.
- Manual and DHCP configuration: Supports both manual configuration of IP addresses and dynamic configuration through DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol).
- Limited address space: The main limitation which has led to the development of IPv6 to cater to more devices.
- Network Address Translation (NAT): Used to allow multiple devices on a private network to share a single public IP address.
- Security: Lacks inherent security features, requiring additional protocols such as IPSec for secure communications.
Drawbacks of IPv4
- Limited Address Space : IPv4 has a limited number of addresses, which is not enough for the growing number of devices connecting to the internet.
- Complex Configuration : IPv4 often requires manual configuration or DHCP to assign addresses, which can be time-consuming and prone to errors.
- Less Efficient Routing : The IPv4 header is more complex, which can slow down data processing and routing.
- Security Issues : IPv4 does not have built-in security features, making it more vulnerable to attacks unless extra security measures are added.
- Limited Support for Quality of Service (QoS) : IPv4 has limited capabilities for prioritizing certain types of data, which can affect the performance of real-time applications like video streaming and VoIP.
- Fragmentation : IPv4 allows routers to fragment packets, which can lead to inefficiencies and increased chances of data being lost or corrupted.
- Broadcasting Overhead : IPv4 uses broadcasting to communicate with multiple devices on a network, which can create unnecessary network traffic and reduce performance.

What is IPv6?
Another most common version of the Internet Protocol currently is IPv6. The well-known IPv6 protocol is being used and deployed more often, especially in mobile phone markets. IPv6 was designed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) in December 1998 with the purpose of superseding IPv4 due to the global exponentially growing internet of users.
IPv6 stands for Internet Protocol version 6. IPv6 is the new version of Internet Protocol, which is way better than IPv4 in terms of complexity and efficiency. IPv6 is written as a group of 8 hexadecimal numbers separated by colon (:). It can be written as 128 bits of 0s and 1s.
IPv6 Address Format is a 128-bit IP Address, which is written in a group of 8 hexadecimal numbers separated by colon (:).
 IPv6 Address Format
IPv6 Address Format To switch from IPv4 to IPv6, there are several strategies:
- Dual Stacking : Devices can use both IPv4 and IPv6 at the same time. This way, they can talk to networks and devices using either version.
- Tunneling : This method allows IPv6 users to send data through an IPv4 network to reach other IPv6 users. Think of it as creating a "tunnel" for IPv6 traffic through the older IPv4 system.
- Network Address Translation (NAT) : NAT helps devices using different versions of IP addresses (IPv4 and IPv6) to communicate with each other by translating the addresses so they understand each other.
Characteristics of IPv6
- IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses, offering a much larger address space than IPv4's 32-bit system.
- IPv6 addresses use a combination of numbers and letters separated by colons, allowing for more unique addresses.
- The IPv6 header has fewer fields, making it more efficient for routers to process.
- IPv6 supports Unicast, Multicast, and Anycast, but no Broadcast, reducing network traffic.
- IPv6 allows flexible subnetting (VLSM) to divide networks based on specific needs.
- IPv6 uses Neighbor Discovery for MAC address resolution instead of ARP.
- IPv6 uses advanced routing protocols like OSPFv3 and RIPng for better address handling.
- IPv6 devices can self-assign IP addresses using SLAAC, or use DHCPv6 for more control.
- IPv6 handles fragmentation at the sender side, not by routers, improving speed.
Difference Between IPv4 and IPv6
| IPv4 | IPv6 |
|---|
| IPv4 has a 32-bit address length | IPv6 has a 128-bit address length |
| It Supports Manual and DHCP address configuration | It supports Auto and renumbering address configuration |
| In IPv4 end to end, connection integrity is Unachievable | In IPv6 end-to-end, connection integrity is Achievable |
| It can generate 4.29x10 9 address space | The address space of IPv6 is quite large it can produce 3.4x10 38 address space |
| The Security feature is dependent on the application | IPSEC is an inbuilt security feature in the IPv6 protocol |
| Address representation of IPv4 is in decimal | Address representation of IPv6 is in hexadecimal |
| Fragmentation performed by Sender and forwarding routers | In IPv6 fragmentation is performed only by the sender |
| In IPv4 Packet flow identification is not available | In IPv6 packet flow identification are Available and uses the flow label field in the header |
| In IPv4 checksum field is available | In IPv6 checksum field is not available |
| It has a broadcast Message Transmission Scheme | In IPv6 multicast and anycast message transmission scheme is available |
| In IPv4 Encryption and Authentication facility not provided | In IPv6 Encryption and Authentication are provided
|
| IPv4 has a header of 20-60 bytes. | IPv6 has a header of 40 bytes fixed
|
| IPv4 can be converted to IPv6 | Not all IPv6 can be converted to IPv4 |
| IPv4 consists of 4 fields which are separated by addresses dot (.) | IPv6 consists of 8 fields, which are separated by a colon (:) |
| IPv4's IP addresses are divided into five different classes. Class A , Class B, Class C, Class D , Class E. | IPv6 does not have any classes of the IP address. |
| IPv4 supports VLSM( Variable Length subnet mask ). | IPv6 does not support VLSM. |
| Example of IPv4: 66.94.29.13 | Example of IPv6: 2001:0000:3238:DFE1:0063:0000:0000:FEFB |
Benefits of IPv6 over IPv4
The recent Version of IP IPv6 has a greater advantage over IPv4. Here are some of the mentioned benefits:
- Larger Address Space: IPv6 has a greater address space than IPv4, which is required for expanding the IP Connected Devices. IPv6 has 128 bit IP Address rather and IPv4 has a 32-bit Address.
- Improved Security: IPv6 has some improved security which is built in with it. IPv6 offers security like Data Authentication, Data Encryption, etc. Here, an Internet Connection is more Secure.
- Simplified Header Format: As compared to IPv4, IPv6 has a simpler and more effective header Structure, which is more cost-effective and also increases the speed of Internet Connection.
- Prioritize: IPv6 contains stronger and more reliable support for QoS features, which helps in increasing traffic over websites and increases audio and video quality on pages.
- Improved Support for Mobile Devices: IPv6 has increased and better support for Mobile Devices. It helps in making quick connections over other Mobile Devices and in a safer way than IPv4.
Why IPv4 is Still in Use?
- Infrastructure Compatibility Many systems and devices are built for IPv4 and require significant updates to support IPv6, including routers, switches, and computers.
- Cost of Transition - Switching to IPv6 can be expensive and complex, involving hardware updates, software upgrades, and training for personnel.
- Lack of Immediate Need - Techniques like NAT (Network Address Translation) help extend the life of IPv4 by allowing multiple devices to share a single public IP address, reducing the urgency to switch to IPv6.
- Coexistence Strategies - Technologies that allow IPv4 and IPv6 to run simultaneously make it easier for organizations to adopt IPv6 gradually while maintaining their existing IPv4 systems.
- Slow Global Adoption - The adoption of IPv6 varies significantly around the world, which necessitates the continued support of IPv4 for global connectivity.
- Lack of Visible Benefits - Many users and organizations don't see immediate improvements with IPv6 if they don't face an IP address shortage, reducing the incentive to upgrade.
Conclusion
The shift from IPv4 to IPv6 is more than just an expansion of address space; it represents a necessary evolution in internet architecture to accommodate future growth and innovation. Understanding these differences helps not only in appreciating how the internet works but also in foreseeing how technology will continue to evolve to meet the needs of an increasingly connected world.
Similar Reads
CCNA Tutorial for Beginners This CCNA Tutorial is well-suited for the beginner as well as professionals, and It will cover all the basic to advanced concepts of CCNA like Components of Computer Networking, Transport Layer, Network Layer, CCNA training, Cisco Networking, Network Design, Routing and Switching, etc. which are req
8 min read
Basics of Computer Networking
Components of Computer Networking
NIC Full Form - Network Interface CardNIC stands for Network Interface Card. NIC is additionally called Ethernet or physical or network card. NIC is one of the major and imperative components of associating a gadget with the network. Each gadget that must be associated with a network must have a network interface card. Even the switches
4 min read
What is a Network Switch and How Does it Work?The Switch is a network device that is used to segment the networks into different subnetworks called subnets or LAN segments. It is responsible for filtering and forwarding the packets between LAN segments based on MAC address. Switches have many ports, and when data arrives at any port, the destin
9 min read
What is Network Hub and How it Works?Hub in networking plays a vital role in data transmission and broadcasting. A hub is a hardware device used at the physical layer to connect multiple devices in the network. Hubs are widely used to connect LANs. A hub has multiple ports. Unlike a switch, a hub cannot filter the data, i.e. it cannot
6 min read
Introduction of a RouterNetwork devices are physical devices that allow hardware on a computer network to communicate and interact with one another. For example Repeater, Hub, Bridge, Switch, Routers, Gateway, Router, and NIC, etc. What is a Router?A Router is a networking device that forwards data packets between computer
12 min read
Types of Ethernet CableAn ethernet cable allows the user to connect their devices such as computers, mobile phones, routers, etc, to a Local Area Network (LAN) that will allow a user to have internet access, and able to communicate with each other through a wired connection. It also carries broadband signals between devic
5 min read
Transport Layer
Transport Layer responsibilitiesThe transport Layer is the second layer in the TCP/IP model and the fourth layer in the OSI model. It is an end-to-end layer used to deliver messages to a host. It is termed an end-to-end layer because it provides a point-to-point connection rather than hop-to-hop, between the source host and destin
5 min read
Introduction of Ports in ComputersA port is basically a physical docking point which is basically used to connect the external devices to the computer, or we can say that A port act as an interface between the computer and the external devices, e.g., we can connect hard drives, printers to the computer with the help of ports. Featur
3 min read
What is TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)?Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is a connection-oriented protocol for communications that helps in the exchange of messages between different devices over a network. It is one of the main protocols of the TCP/IP suite. In OSI model, it operates at the transport layer(Layer 4). It lies between th
5 min read
TCP 3-Way Handshake ProcessThe TCP 3-Way Handshake is a fundamental process that establishes a reliable connection between two devices over a TCP/IP network. It involves three steps: SYN (Synchronize), SYN-ACK (Synchronize-Acknowledge), and ACK (Acknowledge). During the handshake, the client and server exchange initial sequen
6 min read
User Datagram Protocol (UDP)User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is a Transport Layer protocol. UDP is a part of the Internet Protocol suite, referred to as UDP/IP suite. Unlike TCP, it is an unreliable and connectionless protocol. So, there is no need to establish a connection before data transfer. The UDP helps to establish low-late
10 min read
Network Layer
IPv4 Addressing
Subnetting
Data Link Layer
Physical Layer
Cisco Networking Devices
Network Devices (Hub, Repeater, Bridge, Switch, Router, Gateways and Brouter)Network devices are physical devices that allow hardware on a computer network to communicate and interact with each other. Network devices like hubs, repeaters, bridges, switches, routers, gateways, and brouter help manage and direct data flow in a network. They ensure efficient communication betwe
9 min read
Collision Detection in CSMA/CDCSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access/ Collision Detection) is a media access control method that was widely used in Early Ethernet technology/LANs when there used to be shared Bus Topology and each node ( Computers) was connected by Coaxial Cables. Nowadays Ethernet is Full Duplex and Topology is
7 min read
Collision Domain and Broadcast Domain in Computer NetworkPrerequisite - Network Devices, Transmission Modes The most common network devices used are routers and switches. But we still hear people talking about hubs, repeaters, and bridges. Do you ever wonder why these former devices are preferred over the latter ones? One reason could be: 'because they ar
5 min read
Difference between layer-2 and layer-3 switchesA switch is a device that sends a data packet to a local network. What is the advantage of a hub? A hub floods the network with the packet and only the destination system receives that packet while others just drop due to which the traffic increases a lot. To solve this problem switch came into the
5 min read