Difference Between Connection-oriented and Connection-less Services
Last Updated : 28 Dec, 2024
In computer networks, communication between devices occurs using two types of services: connection-oriented and connectionless. These services define how data is transferred between a source and a destination. Connection-oriented services establish a dedicated connection before data transfer, ensuring reliability. In contrast, connectionless services do not establish a connection, sending data without acknowledgment or error correction.
This article explores the differences between connection-oriented and connectionless services, including their definitions, characteristics, advantages, and applications.
What is a Connection-Oriented Service?
Connection-oriented services involve setting up a dedicated path between the source and destination before data transfer begins. These services ensure that data is delivered in the correct sequence and without errors. In a connection-oriented service, the Handshake method is used to establish the connection between sender and receiver. Before data transmission starts, connection-oriented services create a dedicated communication channel between the sender and the recipient. As the connection is kept open until all data is successfully transferred, this guarantees dependable data delivery. One example is TCP (Transmission Control Protocol), which ensures error-free and accurate data packet delivery.
Examples of Connection-Oriented Services
- TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) in the TCP/IP suite.
- Telephone calls in traditional telecommunication systems.
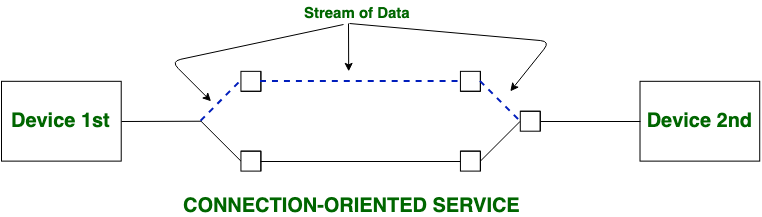
Key Features of Connection-Oriented Services
- Dedicated Connection : A logical or physical connection is established before data transfer.
- Reliable Transmission : Data is transmitted with error checking, acknowledgments, and retransmissions in case of errors.
- Sequencing : Data packets arrive at the destination in the correct order.
- Higher Overhead : Establishing and maintaining a connection involves additional overhead.
Advantages of Connection-Oriented Services
- Reliable Data Transfer : Ensures that all data reaches its destination without errors.
- Data Sequencing : Packets are delivered in the correct order.
- Error Correction : Mechanisms are in place to detect and correct errors during transmission.
- Guaranteed Delivery : Retransmissions occur if data is lost.
Disadvantages of Connection-Oriented Services
- Higher Latency : Establishing a connection adds latency before data transfer begins.
- More Overhead : Requires more resources for maintaining the connection, acknowledgments, and retransmissions.
- Less Efficient for Small Transfers : For short messages, the overhead of connection setup can outweigh the benefits.
What is Connection-Less Service?
Connectionless services send data without establishing a dedicated connection between the source and destination. Each data packet is treated independently, and there is no guarantee of delivery or sequencing. Connection-less Service does not give a guarantee of reliability. In this, Packets do not follow the same path to reach their destination. Connectionless Services deliver individual data packets without first making a connection. Since each packet is sent separately, delivery, order, and mistake correction cannot be guaranteed. As a result, the service is quicker but less dependable. UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is one example, which is frequently used for streaming where dependability is not as important as speed.
Examples of Connectionless Services
- UDP (User Datagram Protocol) in the TCP/IP suite.
- Postal services (analogous to sending letters without confirmation of receipt).

Key Features of Connectionless Services
- No Connection Setup : Data is sent directly without establishing a prior connection.
- Independent Packets : Each packet is treated individually and may take different routes to the destination.
- Faster Transmission : No time is spent establishing or tearing down a connection.
- Unreliable : No acknowledgment, retransmission, or error correction is performed.
Advantages of Connectionless Services
- Low Latency : Data is transmitted immediately without waiting for a connection to be established.
- Efficient for Small Transfers : Ideal for small, time-sensitive messages like DNS lookups or VoIP.
- Scalable : Suitable for systems with many simultaneous users, as no connection needs to be maintained.
Disadvantages of Connectionless Services
- Unreliable : Data packets may be lost, duplicated, or arrive out of order.
- No Error Handling : No built-in mechanisms for retransmissions or error correction.
- Unsuitable for Large Transfers : Not ideal for applications requiring reliable and ordered delivery.
Difference Between Connection-oriented and Connectionless Services
| Connection-oriented Service | Connection-less Service |
|---|
| Connection-oriented service is related to the telephone system. | Connection-less service is related to the postal system. |
| Connection-oriented service is preferred by long and steady communication. | Connection-less Service is preferred by bursty communication. |
| Connection-oriented Service is necessary. | Connection-less Service is not compulsory. |
| Connection-oriented Service is feasible. | Connection-less Service is not feasible. |
| In connection-oriented Service, Congestion is not possible. | In connection-less Service, Congestion is possible. |
| Connection-oriented Service gives the guarantee of reliability. | Connection-less Service does not give a guarantee of reliability. |
Includes error detection, correction, and retransmission. | No error handling; errors are not corrected. |
| In connection-oriented Service, Packets follow the same route. | In connection-less Service, Packets do not follow the same route. |
Ensures data is delivered in the correct order. | Data may arrive out of order or not at all. |
Less scalable due to the need for maintaining connections. | Highly scalable for large networks with many users. |
Higher overhead due to connection setup and maintenance. | Lower overhead as no connection is required. |
| Connection-oriented services require a bandwidth of a high range. | Connection-less Service requires a bandwidth of low range. |
| Ex: TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) | Ex: UDP (User Datagram Protocol) |
| Connection-oriented requires authentication. | Connection-less Service does not require authentication. |
Conclusion
Both connection-oriented and connectionless services are essential for modern networking, each suited to different applications:
- Connection-Oriented Services: Prioritize reliability, sequencing, and error correction, making them ideal for applications like file transfers, email, and telecommunication.
- Connectionless Services: Focus on speed and efficiency, perfect for time-sensitive applications like DNS lookups, VoIP, and online gaming.
The choice of service depends on the specific requirements of the application, such as reliability, speed, and data size.