Combinational and Sequential Circuits
Last Updated : 03 May, 2025
Digital logic circuits are fundamental components in modern electronic devices, enabling operations in systems like computers, mobile phones and calculators by processing binary data through logic gates such as AND, OR and NOT. These circuits are essential for tasks like data storage, decision-making and control functions.
These circuits are primarily classified into two categories: combinational and sequential circuits. Combinational circuits produce outputs based solely on the current inputs while sequential circuits, built with both combinational circuits and memory elements like flip-flops, generate outputs dependent on both the current and previous states.
Combinational Circuits
Combinational logic circuits are made from basic logic gates like AND, OR, and NOT or from universal gates like NAND and NOR. These gates are connected together to create more complex circuits.
 Combinational Circuit
Combinational CircuitIn combinational circuits, the output at any given time depends only on the current inputs not on past states. Since these circuits are not dependent upon previous input to generate any output, so are combinational logic circuits. These circuits are fundamental in performing tasks like arithmetic operations, data routing and comparison.
Classification of Combinational Circuits
 Combinational circuits
Combinational circuitsCombinational circuits can be divided into three main categories:
- Arithmetic or Logical Functions: These circuits perform mathematical or logical operations, such as addition, subtraction, and comparison.
- Data Transmission: These circuits are used for routing and controlling data flow between different parts of a system, ensuring proper data transfer.
- Code Converters: These circuits convert data from one format or code to another, such as converting binary to decimal or vice versa.
Read more about Combinational Circuits in Digital Logic
Sequential Circuits
Sequential logic differs from combinational logic in that its output depends on both the current inputs and its previous states. This means that sequential logic devices have memory, storing part of their "history" to influence future outputs.
A Sequential Logic Circuit consists of two main parts:
- Memory Elements: These are typically flip-flops, which are made up of a combination of logic gates and store the circuit's state.
- Combinational Logic: This part generates the excitation inputs to the memory elements and produces the required outputs based on both current inputs and the stored state.
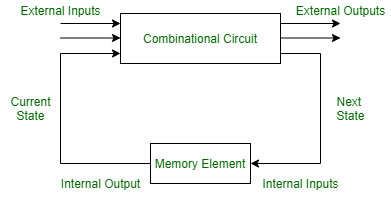 Sequential Circuit
Sequential Circuit- The memory elements are circuits capable of storing binary information.
- The binary information stored in these memory elements at any given time defines the state of the sequential circuit at that time.
- The external output of a sequential circuit depends both on the present input and the previous output state.
- The next state of the memory elements also depends on the external input and the present state of the external output.
- Some sequential circuits may not contain combinational circuits, but only memory elements.
Types of Sequential Circuits
 Sequential Circuits
Sequential CircuitsSequential logic circuits are divided into two types:
- Synchronous Sequential Circuits: In these circuits, the memory contents change only at specific times, triggered by clock transitions. Since the operation of the circuit is controlled by a clock, these circuits are also known as clocked sequential circuits.
- Asynchronous Sequential Circuits: In these circuits, the output can change at any time as a result of changes in the inputs. The memory elements used are delay-type, and the circuit can be considered a combinational circuit with feedback.
Read more about Sequential Circuits in Digital Logic
Difference Between Combinational and Sequential Circuits
| Aspect | Combinational Circuit | Sequential Circuit |
|---|
| Definition | Output depends only on current inputs. | Output depends on both current inputs and past states. |
| Memory Elements | Does not require memory elements. | Requires memory elements (e.g., flip-flops). |
| Clock Signal | No clock signal required. | Requires a clock signal to synchronize state changes. |
| Design Complexity | Simpler design, no memory required. | More complex due to memory and clock management. |
| Examples | Adders, Subtractors, Multiplexers. | Counters, Shift Registers, Flip-Flops. |
Read more about Difference between Combinational and Sequential Circuit