chrt command in Linux with examples
Last Updated : 23 Sep, 2024
'chrt' command in Linux is known for manipulating the real-time attributes of a process. It sets or retrieves the real-time scheduling attributes of an existing PID, or runs the command with the given attributes. 'chrt' can help optimize process management in a Linux system, especially for applications that require real-time performance.
Syntax
$ chrt [options] priority command [argument ...]
$ chrt [options] -p [priority] pid
where,
- priority: The scheduling priority for the process (if applicable).
- command: The command to be executed with the specified scheduling attributes.
- pid: The process ID of the existing process you want to manipulate.
Note: The 'chrt' command typically requires root privileges to modify scheduling policies for existing processes.
Common Options with 'chrt' command
| Option | Description |
|---|
-b, --batch | Sets the policy to SCHED_BATCH. |
|---|
-d, --deadline | Sets the policy to SCHED_DEADLINE. |
|---|
-f, --fifo | Sets the policy to SCHED_FIFO. |
|---|
-i, --idle | Sets the policy to SCHED_IDLE. |
|---|
-o, --other | Sets the policy to SCHED_OTHER (default time-sharing). |
|---|
-r, --rr | Sets the policy to SCHED_RR (default real-time policy). |
|---|
-p, --pid | Operates on an existing process with the specified pid. |
|---|
-a, --all-tasks | Operates on all tasks (threads) for a given pid. |
|---|
-m, --max | Displays the minimum and maximum valid priorities for the policies. |
|---|
-v, --verbose | Displays status information. |
|---|
-h, --help | Displays help information and exits. |
|---|
--version | Displays version information and exits |
|---|
Scheduling Options with 'chrt' Command
- SCHED_BATCH : Use Scheduling batch processes algorithm.
- SCHED_FIFO : Uses First In-First Out scheduling algorithm. This scheduling method is used on Batch-Systems, it is NON-PREEMPTIVE. It implements just one queue which holds the tasks in the order they come in.
- SCHED_IDLE: Used for running very low priority background jobs.
- SCHED_OTHER: Uses Default Linux time-sharing scheduling algorithm or simply the standard round-robin time-sharing policy.
- SCHED_RR Uses Round Robin scheduling algorithm and is used as the default algorithm if not specified. It is an algorithm used for PREEMPTIVE scheduling.
chrt Command Examples in Linux
Here are some examples of how to use chrt to manage real-time scheduling:
1. To see the current scheduling policy:
First we have to make a process. Let's take a example, Firefox is running and to find its's pid we run the following command:
$ pidof -s firefox
In my case the pid is 5794, here is the image

Now to retrieve the current scheduling policy and priority for the firefox process, use chrt in the following way:
$ chrt -p 5794

2. To change the scheduling policy to SCHED_FIFO:
From the above example, the scheduling policy of firefox process is set as SCHED_OTHER. Now to change the policy to SCHED_FIFO we can use the following command:
$ sudo chrt -f -p 5794

3. To change the scheduling policy SCHED_BATCH:
From the above example, the scheduling policy of the firefox process is set as SCHED_FIFO. Now to change the policy to SCHED_BATCH we can use the following command:
$ sudo chrt -b -p 5794

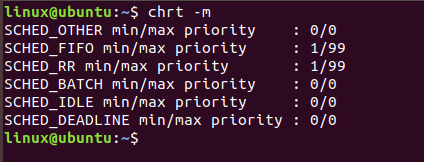
4. To see the maximum and minimum valid priorities:
This can be done using the -m command line option mentioned in the policy of chrt.
$ chrt -m
Conclusion
The 'chrt' command in Linux is a powerful tool for controlling the scheduling attributes of processes. By understanding how to use it effectively, you can optimize system performance for real-time tasks or background jobs, depending on your specific needs. 'chrt' allows you to fine-tune how these processes are scheduled, ensuring that critical tasks are prioritized appropriately while preventing less important tasks from consuming excessive system resources.
Similar Reads
cc command in Linux with Examples 'cc' command stands for C Compiler, usually an alias command to 'gcc' or 'clang'. As the name suggests, executing the 'cc' command will usually call the 'gcc' on Linux systems. It is used to compile the C language codes and create executables. The number of options available for the cc command is ve
3 min read
Encrypt/Decrypt Files in Linux using Ccrypt Ccrypt is a command line tool for encryption and decryption of data. Ccrypt is based on the Rijndael cipher, the same cipher used in the AES standard. On the other hand, in the AES standard, a 128-bit block size is used, whereas ccrypt uses a 256-bit block size. Ccrypt commonly uses the .cpt file ex
3 min read
How to Change the Directory in Linux | cd Command Navigating the Linux file system is like exploring a vast library; each directory (folder) holds its own collection of files and subdirectories, and knowing how to move between them efficiently is the first step to mastering the command line. The cd (Change Directory) command is your compass in this
7 min read
cfdisk command in Linux with examples cfdisk command is used to create, delete, and modify partitions on a disk device. It displays or manipulates the disk partition table by providing a text-based "graphical" interface. cfdisk /dev/sda Example: After running you get a prompt like this: Choose gpt from the list. Now you will see a parti
3 min read
chage command in Linux with examples The 'chage' command in Linux is a powerful tool used to manage user password expiry and account aging information. It is particularly useful in environments where user access needs to be controlled over time, such as when login access is time-bound or when it’s necessary to enforce regular password
4 min read
chattr and lsattr commands in Linux with examples In the world of Linux, managing file permissions and attributes is crucial for maintaining a secure and organized system. Two powerful commands that help control file and directory attributes are 'chattr' and 'lsattr'. These commands are essential for administrators and advanced users who need to pr
8 min read
chfn command in Linux with examples 'chfn' command in Linux allows you to change a user's name and other details easily. 'chfn' stands for Change finger. Basically, it is used to modify your finger information on Linux system. This information is generally stored in the file '/etc/passwd' that includes user's original name, work phone
3 min read
chgrp command in Linux with Examples The `chgrp` command in Linux is used to change the group ownership of a file or directory. All files in Linux belong to an owner and a group. You can set the owner by using “chown†command, and the group by the "chgrp" command. Syntax of `chgrp` command in Linuxchgrp [OPTION]… GROUP FILE… chgrp [OPT
3 min read
chkconfig command in Linux with Examples 'chkconfig' command is used to list all available services and view or update their run level settings. In simple words it is used to list current startup information of services or any particular service, update runlevel settings of service, and adding or removing service from management. Here we’l
3 min read
How to Make Script Executable in Linux | chmod Command In Unix operating systems, the chmod command is used to change the access mode of a file. The name is an abbreviation of change mode. Which states that every file and directory has a set of permissions that control the permissions like who can read, write or execute the file. In this the permissions
7 min read