Centripetal acceleration refers to the acceleration experienced by an object moving in a circular route. Unlike linear acceleration, which changes an item's speed in a straight line, centripetal acceleration alters the direction of motion, causing the object to constantly shift its velocity vector in order to maintain circular motion.
There are a lot of objects around us in real life that are constantly performing circular motion, even our planet revolves around the sun in a similar fashion. It is known that velocity is a vector quantity and any object performing circular motion is undergoing a change of velocity. Since there is a change in velocity, a force must be there that acts on the body to change its velocity continuously and make it perform the circular motion. This change in velocity is called acceleration. In this article, we will learn in detail about centripetal acceleration, its formula, derivation, and applications.
What is Centripetal Acceleration?
Centripetal acceleration is the acceleration felt by an object moving on a circular route toward the center of the circle. This acceleration is responsible for shifting the direction of the object's velocity, ensuring that it remains in circular motion.
Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity. Since acceleration and velocity are both vector quantities, they depend on direction. So, either there is a change in the magnitude of the velocity or direction of the velocity. In a circular motion, there is always an acceleration because the velocity of the object is continuously changing. This acceleration is felt whenever a person is turning a car, there is a force acting on the person and the wheel too. The force depends on the radius of the turn and the velocity of the object. This means, the sharper the turn, the more force acts on the body.
The formula for centripetal acceleration is given as
ac = v2/r
where,
- ac is centripetal acceleration
- v is velocity of object moving in circular path
- r is radius of circular path
Acceleration points towards the center of the curvature, now since the velocity is continuously changing and acceleration is present. This acceleration is called centripetal acceleration ac. Here, centripetal means "center seeking" or "toward the center". Let's derive the equation for calculating the magnitude of the centripetal force.
The figure given below shows an object which is moving in a circular motion. Assume that the speed of the object is constant. The figure shows the direction of the instantaneous velocity and points B and C. Since acceleration is the change in velocity, the change in velocity is roughly pointing towards the center of the curvature. To measure things instantaneously, the points B and C must be brought really close together, and the angle between them should be infinitely small. In that case, the change of velocity will point directly towards the center of the curvature.
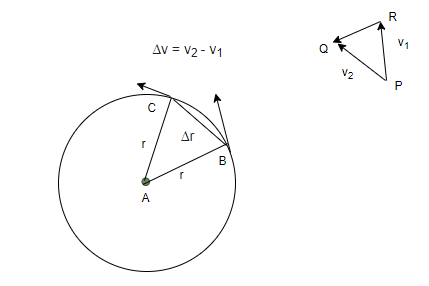
In the figure given above, notice that the triangles ABC and QPR are isosceles triangles. The two sides of the vector velocity triangles are denoted by v1 and v2. Comparing the two triangles using properties of similar triangles,
\frac{\Delta v }{v} = \frac{\Delta s}{r}
The acceleration is given by the change in velocity with respect to time,
\Delta v = \frac{\Delta s}{r} v
Dividing both sides with delta-t
\frac{\Delta v}{\Delta t} = \frac{\Delta s}{r} . \frac{v}{\Delta t}
Rearranging the equation,
\frac{\Delta v}{\Delta t} = \frac{\Delta s}{\Delta t} . \frac{v}{r}
Note that Δv/Δt is the ac and Δs/Δt is the tangential speed (v).
So, the centripetal acceleration becomes,
a = v2/r
This gives us the acceleration of an object under the circular motion traveling at a speed "v" and with radius "r". This equation depends on the square of the velocity and inversely to the radius "r".
Characteristics of Centripetal Acceleration
The characteristic of centripetal acceleration is given below:
- Centripetal acceleration is always directed toward the centre of the circular path. It is perpendicular to the object's velocity vector and points inward in the radial direction.
- The magnitude of centripetal acceleration is proportional to the object's speed and the radius of its circular path. It increases with the square of the speed (v2) and decreases with the radius (r).
- Newton's second law of motion (F=ma) states that centripetal acceleration requires a force acting on the object. This force, known as the centripetal force, is directed toward the center of the circular path and is required to keep the object moving in a circular pattern.
Centripetal Force
Centripetal force is the force that maintains an object moving in a circular direction toward the center of the circle. This force is required to shift the direction of the object's velocity and so maintain the circular motion. The formula for centripetal force is given as
Fc = m.ac
where,
- Fc is Centripetal Force
- m is mass of object
- ac is centripetal acceleration
Application of Centripetal Acceleration
Centripetal acceleration is an important topic in many physics experiments and demonstrations, as it helps to show the principles of uniform circular motion, rotational dynamics, and the link between force, mass, and acceleration.
Circular Motion: Centripetal acceleration is critical for understanding and studying numerous types of circular motion, such as planets orbiting the Sun, satellites orbiting a celestial body, and automobiles traversing curves on roads or tracks.
Rides and Amusement Parks: Roller coasters, carousels, and other amusement park rides frequently use centripetal acceleration to provide exhilarating and dynamic experiences for riders.
Engineering and Design: When developing rotating or circular motion components and systems such as centrifuges, flywheels, and gyroscopes, engineers and designers take centripetal acceleration into consideration.
Also, check
Solved Examples on Centripetal Acceleration
Example 1: Find the centripetal acceleration on an object performing circular motion with a radius of 5m. The velocity of the object is 10m/s.
Solution:
The centripetal acceleration is given by,
a = v2/r
Given:
v = 10m/s.
r = 5m.
Plugging the values in the equation,
a = v2/r
⇒ a = (10)2/(5)
⇒ a = 100/5
⇒ a = 20 m/s2
Example 2: Find the centripetal acceleration on an object performing circular motion with a radius of 20m. The velocity of the object is 100m/s.
Solution:
The centripetal acceleration is given by,
a = v2/r
Given:
v = 100m/s.
r = 20m.
Plugging the values in the equation,
a = v2/r
⇒ a = (100)2/(20)
⇒ a = 10000/20
⇒ a = 500 m/s2
Example 3: An object(m = 5Kg) is performing circular motion with radius 2m. If the velocity of the object is 8 m/s, find the centripetal force acting on the object.
Solution:
The centripetal acceleration is given by,
a = v2/r
Given:
v = 8m/s.
r = 2m.
Plugging the values in the equation,
a = v2/r
⇒ a = (8)2/(2)
⇒ a = 64/2
⇒ a = 32 m/s2
Force acting on the object is given by,
F = ma
⇒ F = (5)(32)
⇒ F = 160 N
Example 4: An object(m = 2Kg) is performing circular motion with radius 5m. If the velocity of the object is 10 m/s, find the centripetal force acting on the object.
Solution:
The centripetal acceleration is given by,
a = v2/r
Given:
v = 10m/s.
r = 5m.
Plugging the values in the equation,
a = v2/r
⇒ a = (10)2/(5)
⇒ a = 100/5
⇒ a = 20 m/s2
Force acting on the object is given by,
F = ma
⇒ F = (2)(20)
⇒ F = 40 N
Example 5: An object(m = 2Kg) is performing circular motion with radius 5m. If the centripetal force acting on the object is 100N, find the velocity of the object.
Solution:
Force acting on the object is given by,
F = ma
⇒ 100 = (2)(a)
⇒ a = 50 m/s2
The acceleration of the object is given by,
a = v2/r
⇒ 50 = v2/5
⇒ 250 = v2
⇒ v = 5√10 m/s.