CBSE Class 11th Unit 3: Society, Law, and Ethics is an essential part of the Computer Science curriculum, designed to equip students with the knowledge and awareness needed to navigate our increasingly digital world. CBSE 2024-25 syllabus, this unit goes beyond just theory—it dives into the real-world impact of technology on society, explores the laws that keep our digital lives in check, and challenges students to think critically about the ethical dilemmas posed by new technologies.
Here’s an overview of the key concepts covered in the CBSE Class 11th CS Unit 3 notes:
- Society: Understanding the influence of technology on social interactions, including how digital platforms shape communication and community dynamics.
- Law: Exploring the legal frameworks that regulate technology, covering areas such as data protection, intellectual property, and cybercrime.
- Ethics: Examining the moral principles guiding the use of technology, focusing on issues like AI decision-making, data privacy, and the digital divide.
- What is a Digital Footprint? Learning about the trail of data left behind by online activities, including its impact on privacy, security, and personal reputation.
- Digital Society: Understanding how digital platforms create interconnected communities, affecting reputation, relationships, and future opportunities.
- Data Protection and Intellectual Property Rights: Studying the importance of safeguarding digital information and the legal protections for creative and innovative works.
- Open Source Software: Exploring software that allows users to inspect, modify, and enhance its code, promoting collaboration and innovation.
- Cyber Crime: Identifying illegal activities conducted through digital means, such as hacking, phishing, and ransomware.
- Malware: Learning about malicious software designed to harm computers or steal data, including viruses, trojans, and adware.
- E-Waste Management: Understanding the proper disposal and recycling of electronic waste to protect the environment and recover valuable materials.
- Information Technology Act (IT Act): Studying India's legal framework for electronic governance, digital transactions, and cybercrime regulation.
- Key Elements of IT Act, 2000: Focusing on legal recognition of electronic records, facilitation of e-governance, and the regulation of cybercrime and data protection.
- Technology and Society: Examining the interplay between technology and societal issues, including gender, disability, and equitable access to digital resources.
 CBSE Class 11th Computer Science Unit 3 Notes: Society, Law and Ethics
CBSE Class 11th Computer Science Unit 3 Notes: Society, Law and EthicsCBSE Class 11th Computer Science Unit 3 Notes: Society, Law and Ethics
Society
- What It Is: Society refers to the community of people living together and how they interact with each other. In the tech world, this includes how technology affects and is affected by social interactions. For instance, social media platforms connect people globally, influencing how we communicate and share information.
- Impact of Technology: Technology changes how we live and work. It can bring people closer together, like video calls with friends or online communities, but it also raises questions about privacy and screen time. Imagine how your smartphone lets you stay in touch with friends, but also think about the time you spend scrolling through social media!
Law
- What It Is: Laws are rules that govern behavior within a society. They ensure everyone follows the same rules and helps resolve conflicts. In tech, laws cover things like intellectual property (who owns ideas and inventions), data protection (how your data is used), and cybercrime (illegal online activities).
- Tech Laws Example: If you download an app, it should follow data protection laws, like not sharing your personal information without your permission. Think of it like a rulebook for how technology should be used responsibly and legally.
Ethics
- What It Is: Ethics involve the moral principles that guide our behavior, distinguishing right from wrong. In tech, ethics tackle issues like AI decision-making, data privacy, and the digital divide (the gap between those who have access to technology and those who don’t).
- Tech Ethics Example: Consider the ethics of AI—should a computer make decisions that affect people’s lives, like hiring or medical diagnoses? It's like trying to decide whether a robot should be allowed to choose your school classes.
Key Points to Remember
- Balancing Act: Technology often presents dilemmas where we must balance benefits and potential drawbacks. For example, the convenience of online shopping must be balanced with concerns about data security.
- Global Impact: Different countries have different laws and ethical standards. What’s considered acceptable in one place might not be in another. It’s like how different cultures have different customs—technology doesn’t work the same way everywhere.
- Staying Informed: As technology evolves, so do laws and ethical guidelines. It’s important to stay updated on how new tech developments impact society and your personal life.
- Definition: Your digital footprint is the record of everything you do online. It includes things like your social media posts, the websites you visit, and even the data collected by apps. Think of it like a diary of your online activities, but it’s visible to others and can last a long time.
- Types of Digital Footprints:
- Active Footprint: This includes things you do intentionally, like posting photos on Instagram or writing a blog. It's like sending postcards to friends you're directly sharing your experiences.
- Passive Footprint: This is data collected without your direct action, like tracking cookies on websites or location data from your phone. It’s like someone secretly noting where you’ve been and what you’re interested in.
Why It Matters
- Privacy: Your digital footprint can impact your privacy. For example, a potential employer might search your name online before an interview. If there are embarrassing posts or information that doesn’t reflect well on you, it could affect their impression.
- Security: A large digital footprint can make you more vulnerable to hacking or identity theft. It’s like leaving your house keys under the doormat—easy for someone to find and misuse.
- Reputation: Everything you post online contributes to your digital reputation. Just as you wouldn’t want your diary read by everyone, you might not want all your posts and activities visible to everyone.
- Think Before You Click: Before posting something, ask yourself if you’d be comfortable with everyone seeing it. It’s like deciding if you’d want a photo of yourself in pajamas to be shared with the world.
- Check Privacy Settings: Regularly review and adjust the privacy settings on your social media accounts. It’s like locking your diary so only those you trust can read it.
- Be Cautious with Apps and Websites: Only share your information with trusted sites and apps. Just as you wouldn’t share your personal secrets with a stranger, be careful about where you input personal data online.
- Regular Clean-Up: Periodically search your name online to see what information is available about you. If you find anything you’d like to remove, take steps to delete or update it.
Real-World Example
Think of your digital footprint like a trail of footprints in the sand. If you’re walking along a beach, your footprints are left behind, showing where you’ve been. Some of these footprints might be just a part of your day at the beach, while others might reveal a bit more about your activities. Just as you wouldn’t want someone to misinterpret your footprints, you don’t want your digital footprint to misrepresent you.
Digital Society
- What It Is: A digital society refers to a community that interacts and communicates through digital platforms like social media, forums, and messaging apps. It’s like being part of a global neighborhood where everything happens online.
- Importance: In a digital society, how you interact online can affect your reputation, relationships, and even your future opportunities. Just as you follow social rules in person, there are digital rules to follow to make online interactions smooth and respectful.
Net Etiquette
- What It Is: Net etiquette, or netiquette, is the set of rules for behaving well online. It’s like having manners for the internet, ensuring that everyone has a positive experience.
- Examples:
- Be Polite: Just like in face-to-face conversations, be respectful and kind in your messages and posts. Saying “please” and “thank you” goes a long way.
- Avoid SHOUTING: Using all caps in online communication can come across as shouting. So, use regular capitalization to keep things calm and friendly.
- Respect Privacy: Don’t share other people’s private information or conversations without permission. It’s similar to not discussing someone’s personal life in public.
Communication Etiquette
- What It Is: Communication etiquette covers the manners and guidelines for effective and respectful online communication. It ensures that your messages are clear and considerate.
- Examples:
- Be Clear and Concise: Write in a way that’s easy to understand. Avoid using too much jargon or complex language. It’s like giving clear instructions so your friend knows exactly what you mean.
- Respond in a Timely Manner: If someone reaches out to you, try to respond within a reasonable time. It shows you value their communication, much like replying to a text from a friend promptly.
- Use Emojis Wisely: Emojis can help express emotions but don’t overuse them. They’re like the facial expressions in a face-to-face conversation—use them to add context, not to replace words.
- What It Is: Social media etiquette involves how to behave on platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter. It’s about maintaining a positive online presence and interacting respectfully.
- Examples:
- Think Before You Post: Before sharing something, consider if it’s appropriate and if it could affect others. It’s like checking if a joke is suitable before telling it in front of a group.
- Tagging and Mentioning: Tag people or mention them only if it’s relevant to them and if you have their consent. It’s like making sure your friends are okay with being included in a group photo before posting it.
- Avoid Overposting: Posting too frequently can overwhelm your followers. Think of it like not dominating a conversation share interesting content, but don’t flood everyone’s feed.
Real-World Example
Imagine your online interactions as hosting a party. You want to make sure your guests are comfortable, enjoy themselves, and feel respected. Following netiquette, communication etiquette, and social media manners is like being a great host making sure everyone has a good time and feels valued.
Being a good netizen involves understanding and applying these digital manners to ensure everyone has a pleasant experience online. Just as you’d be considerate and respectful in person, do the same in your digital interactions.
Data Protection and Intellectual Property Rights
Data Protection and Intellectual Property Rights (IPR)
- What It Is: Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) are legal protections for creations of the mind, including inventions, literary and artistic works, symbols, names, and images used in commerce. They ensure creators and inventors can control and benefit from their creations.
Types of Intellectual Property Rights
- Copyright
- What It Is: Copyright protects original works of authorship, like books, music, films, and software. If you write a story or create a painting, copyright gives you the right to control how it’s used and shared.
- Example: Imagine you’ve written a cool short story. Copyright means that others can’t publish or copy your story without your permission.
- Patent
- What It Is: Patents protect new inventions or discoveries, giving the inventor exclusive rights to make, use, or sell their invention for a set period (usually 20 years). It’s like a reward for inventing something new.
- Example: If you invent a new type of smartphone that folds in a unique way, a patent would prevent others from making or selling your design without your consent.
- Trademark
- What It Is: Trademarks protect brands, logos, and symbols that distinguish goods or services. It’s like a unique stamp that identifies the source of a product.
- Example: The Nike “swoosh” logo is a trademark. It tells you that the product is from Nike and not from another company.
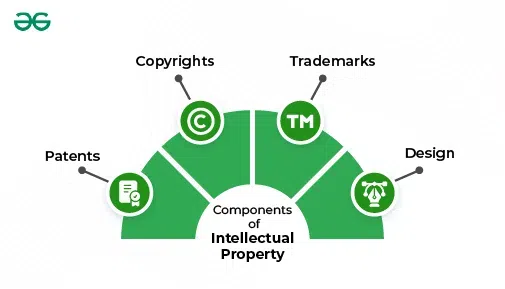 IPR Components
IPR ComponentsViolations of Intellectual Property Rights
- Plagiarism
- What It Is: Plagiarism is the act of using someone else’s work or ideas without proper acknowledgment. It’s like copying a friend’s homework and pretending it’s your own.
- Example: If you copy a paragraph from an article and include it in your own paper without citing the source, that’s plagiarism.
- Copyright Infringement
- What It Is: Copyright infringement occurs when someone uses a copyrighted work without permission. It’s like downloading a movie or music illegally.
- Example: Sharing a music file you downloaded from an illegal site is copyright infringement because you’re using someone’s work without their consent.
- Trademark Infringement
- What It Is: Trademark infringement happens when someone uses a trademark that’s similar enough to cause confusion with the original brand. It’s like creating a logo that looks too much like the original Nike swoosh.
- Example: If you start a clothing line and use a logo that looks a lot like the Nike swoosh, that could be trademark infringement.
Why It Matters
- Protecting Creativity: IPR helps protect the hard work and innovation of creators and inventors. It ensures they get credit and rewards for their efforts, much like how you’d want to be acknowledged for your project or idea.
- Avoiding Legal Trouble: Violating IPR can lead to legal consequences, including fines and legal action. It’s like getting caught cheating on an exam you could face serious repercussions.
- Encouraging Innovation: By respecting IPR, we support and encourage new ideas and creativity. It’s like applauding someone who invents a new game, making them want to create even more.
Real-World Example
Imagine you’re a student who writes a fantastic story. Copyright ensures that no one can publish it as their own. If someone does copy it without permission, they’re infringing on your rights. Think of IPR as the rules of a game that help everyone play fair and respect each other's contributions.
Open Source Software
- What It Is: Open source software (OSS) is software with source code that anyone can inspect, modify, and enhance. It’s like having a recipe that you can tweak to suit your taste or even share with friends. The idea is that the more people work on it, the better it becomes.
- Examples: Popular examples of open source software include the Mozilla Firefox browser, the LibreOffice suite, and the Linux operating system. These tools are developed and maintained by communities of volunteers and organizations.
Types of Open Source Licenses
- Creative Commons (CC)
- What It Is: Creative Commons licenses are used mainly for creative works like art, music, and writing. They let creators specify how others can use their work. Think of it as setting rules for how your artwork or writing can be shared or adapted.
- Types of CC Licenses:
- CC BY: Allows others to use and modify your work as long as they give you credit.
- CC BY-SA: Allows others to remix your work as long as they share their new creation under the same terms.
- CC BY-ND: Allows others to use your work, but not to modify it.
- Example: If you create a fantastic illustration and choose a CC BY license, others can use and modify your illustration as long as they credit you.
- GNU General Public License (GPL)
- What It Is: The GPL is a license used for software that ensures it remains free and open for everyone to use, modify, and distribute. It’s like a guarantee that the software will stay free and open for everyone who uses it.
- Key Features:
- Copyleft: Any software derived from GPL-licensed software must also be GPL-licensed. This means that improvements or changes made to the software must be shared freely.
- Example: The Linux operating system is licensed under the GPL, meaning anyone can use, modify, and distribute Linux, as long as they also share their changes under the same GPL license.
- Apache License
- What It Is: The Apache License is another open source license that allows users to freely use, modify, and distribute software. It’s a bit more flexible compared to the GPL, allowing for both open and proprietary use.
- Key Features:
- Grants Patent Rights: Provides a patent grant to users, protecting them from patent claims related to the software.
- Compatible with Other Licenses: Can be combined with other licenses more easily than GPL.
- Example: The Apache HTTP Server is licensed under the Apache License, meaning developers can use and modify the server software while integrating it into both open source and proprietary projects.
Why It Matters
- Freedom to Innovate: Open source software and licenses encourage innovation by allowing anyone to contribute and build upon existing projects. It’s like a group project where everyone’s ideas can make the final result better.
- Cost-Efficiency: OSS can be a cost-effective option for individuals and organizations since it’s often available for free. It’s like getting a high-quality tool or resource without having to pay for it.
- Community Collaboration: Open source projects often involve vibrant communities of users and developers who help each other and improve the software collectively. It’s like being part of a club where everyone shares their skills and knowledge to create something amazing.
Real-World Example
Imagine you’re part of a school project where everyone contributes different sections to a report. An open source license is like agreeing on how the final report can be used and shared—whether others can add to it, modify it, or use it in other ways. Creative Commons might let others share your work as long as they credit you, GPL ensures any changes made are also shared freely, and Apache gives flexibility while also protecting against patent issues.
Understanding these licenses helps you know how you can use, share, and contribute to software and creative works responsibly. It’s all about respecting others’ work while also benefiting from a collaborative and open environment.
Cyber Crime
- What It Is: Cyber crime involves illegal activities conducted through computers or the internet. It’s like using technology for bad purposes, such as stealing personal information, causing harm, or spreading misinformation. Just as you wouldn’t want someone to steal your bike or break into your home, you wouldn’t want them to invade your digital life.
Types of Cyber Crime
- Hacking
- What It Is: Hacking is when someone gains unauthorized access to a computer system or network. Think of it as breaking into a house without permission. Hackers might do this to steal data, cause damage, or just for fun.
 Hacking
Hacking- Example: Imagine someone sneaking into your email account and reading your private messages without your knowledge. That’s a form of hacking.
2. Eavesdropping
- What It Is: Eavesdropping involves secretly listening to or intercepting private communications. It’s like someone overhearing your private conversation without you knowing.
- Example: If someone intercepts your messages while they’re being sent over the internet, they could steal sensitive information or spy on you.
3. Phishing and Fraud Emails
- What It Is: Phishing is when scammers send fake emails or messages pretending to be someone trustworthy to steal personal information. It’s like someone pretending to be a bank representative to trick you into giving them your account details.
- Example: You receive an email that looks like it’s from your bank asking you to click a link and provide your password. If you do, the scammers can access your bank account.
 Phishing
Phishing4. Ransomware
- What It Is: Ransomware is a type of malicious software that locks or encrypts a victim’s data, demanding payment (a ransom) to unlock it. It’s like someone putting a padlock on your locker and demanding money to give you the key.
- Example: If a ransomware attack encrypts all your files and demands payment in cryptocurrency to unlock them, that’s a ransomware attack.
5. Cyber Trolls
- What It Is: Cyber trolls are people who deliberately post inflammatory or offensive comments online to provoke others or cause chaos. It’s like someone starting a fight at a party just for fun.
- Example: If someone posts rude or misleading comments on social media just to upset others or get attention, that’s trolling.
6. Cyberbullying
- What It Is: Cyberbullying involves using digital platforms to harass or intimidate someone. It’s like traditional bullying, but it happens online through social media, text messages, or other digital channels.
- Example: If someone repeatedly sends mean messages or posts harmful comments about another person online, that’s cyberbullying.
Why It Matters
- Safety and Security: Understanding these threats helps you protect yourself and your information online. It’s like knowing how to lock your doors and windows to keep your home safe.
- Preventing Harm: By recognizing and avoiding these cyber crimes, you can prevent damage to yourself and others. It’s about staying vigilant and cautious in the digital world.
- Legal Implications: Engaging in or falling victim to cyber crime can have serious legal consequences. Just like breaking the law in the physical world, doing so online can lead to legal trouble.
Real-World Example
Imagine you're at a party and someone secretly listens to your conversations (eavesdropping) or pretends to be a friend to trick you into giving away your personal info (phishing). Later, they might even lock up your important files and demand money to get them back (ransomware). These situations illustrate how cyber crime can invade your digital space just like physical crime does in the real world.
Cyber Safety
Safely Browsing the Web
- Be Cautious with Links: Only click on links from trusted sources. Just like you wouldn’t open a door to a stranger, don’t click on random links. They could lead to malicious sites or install harmful software on your device.
- Use Secure Websites: Look for “https” at the beginning of a website’s URL. The “s” stands for secure, meaning the site uses encryption to protect your data. It’s like having a lock on a door to keep your information safe.
- Keep Software Updated: Regularly update your browser and antivirus software. These updates often include security patches to protect against new threats. It’s like getting new locks and alarms for your house to keep up with the latest security measures.
Identity Protection
- Use Strong Passwords: Create complex passwords using a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid using easily guessable information like your birthday or common words. Think of your password as a sturdy lock, the harder it is to pick, the better.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): 2FA adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of verification in addition to your password. It’s like having both a key and a code to get into a secure room.
- Be Careful with Personal Information: Don’t share sensitive information like your Social Security number or bank details unless you’re absolutely sure the site or person is trustworthy. It’s like only sharing your home address with people you know and trust.
Confidentiality
- Use Privacy Settings: Adjust privacy settings on social media and other online accounts to control who can see your information. It’s like drawing the curtains on your windows so strangers can’t peek inside.
- Be Wary of Public Wi-Fi: Avoid using public Wi-Fi for sensitive activities like online banking. Public networks can be less secure, making it easier for someone to intercept your data. It’s like using a public phone to discuss confidential information risky and not private.
- Log Out When Done: Always log out of accounts when you’re finished, especially on shared or public computers. It’s like locking your front door when you leave home.
Why It Matters
- Protects Your Personal Information: By following these practices, you safeguard your personal and financial information from being stolen or misused. It’s like having a security system to keep your valuables safe.
- Prevents Identity Theft: Identity theft can have serious consequences, including financial loss and damage to your reputation. Keeping your identity protected ensures that your personal details stay yours alone.
- Maintains Online Privacy: Confidentiality ensures that your online activities and personal data are kept private, away from prying eyes. It’s about keeping your digital life as private as your real-life home.
Real-World Example
Imagine you’re at a party and you wouldn’t just hand out your phone number to everyone you meet. Online, it’s similar—be selective about where you share your personal details. If you’re browsing a website and it doesn’t seem secure, or if someone asks for sensitive information, think twice before you click or share. Just like you’d be cautious in the real world, be cautious online to stay safe.
Malware
- What It Is: Malware, short for malicious software, is designed to damage or disrupt your computer, steal information, or spy on you. It’s like having a mischievous troublemaker who tries to mess up your digital life.
Types of Malware
- Viruses
- What They Are: Viruses are programs that attach themselves to other files or programs and spread when those files are shared. They can corrupt or delete your data, or even make your computer run slow. It’s like a sneaky germ that spreads from one person to another, making everyone sick.
- Example: Imagine you download a seemingly harmless file from the internet, but it actually contains a virus. Once you open the file, the virus starts spreading through your computer, causing problems and possibly damaging important files.
- Trojans
- What They Are: Trojans disguise themselves as legitimate software to trick you into installing them. Unlike viruses, they don’t spread on their own but rely on you to open or run them. They can then give attackers access to your system. It’s like a friendly-looking gift box that, when opened, reveals a nasty surprise inside.
- Example: You might download a game or an app that seems perfectly fine, but once you install it, a trojan is secretly installed, giving hackers access to your personal data or control over your computer.
- Adware
- What It Is: Adware displays unwanted advertisements on your computer. While it may not be as harmful as viruses or trojans, it can be very annoying and may slow down your system. It’s like having someone constantly popping up ads and flyers in your face, even when you’re trying to focus on something important.
- Example: You might notice a sudden increase in pop-up ads or unwanted toolbars on your web browser. These are signs of adware, which is cluttering your computer with ads and potentially tracking your online behavior to serve more targeted ads.
Why It Matters
- Protects Your Data: Understanding these types of malware helps you avoid falling victim to them and keeps your personal information safe from theft or damage. Just like you wouldn’t leave your house open to burglars, you wouldn’t leave your computer unprotected from malware.
- Maintains Computer Performance: Malware can slow down your computer or make it behave unpredictably. Keeping your system clean and secure ensures it runs smoothly and efficiently.
- Prevents Privacy Breaches: Some malware can access your personal information, leading to privacy issues. Being aware of these threats helps you safeguard your private data from being compromised.
Real-World Example
Think of your computer like a safe deposit box. If someone slips a virus into your box, it can mess up your valuable documents (files) and make them inaccessible. If a trojan is disguised as a nice gift, it might open the box for someone who shouldn’t have access. And if adware is like an endless stream of annoying flyers, it’s just constantly bothering you without causing major damage but still making your life harder.
E-Waste Managemen
E-Waste Management is all about taking care of your old electronic gadgets in an eco-friendly way. Imagine your old electronics as clutter in your room—how you deal with it can either keep your space tidy or create a mess. Here’s how to properly dispose of used electronic gadgets and why it’s important:
- What It Is: E-waste refers to discarded electronic devices like computers, smartphones, and TVs. Properly managing e-waste means recycling or disposing of these items in a way that’s safe for the environment.
Why It Matters
- Environmental Impact: Electronic gadgets often contain harmful substances like lead, mercury, and cadmium. If not properly disposed of, these chemicals can leach into the soil and water, causing pollution. Proper disposal helps keep these dangerous substances out of our environment.
- Resource Recovery: Electronics are made of valuable materials such as gold, silver, and rare metals. Recycling e-waste allows these materials to be recovered and reused, reducing the need to mine for new resources. It’s like recycling to get back valuable materials and save natural resources.
How to Properly Dispose of E-Waste
- Check for Recycling Programs
- What to Do: Many cities have special recycling programs or centers for e-waste. Check with local waste management services or electronics retailers for drop-off points.
- Example: Your community might have an e-waste recycling event where you can bring old gadgets for safe disposal. It’s like a community cleanup day for electronics!
- Use Manufacturer Take-Back Programs
- What to Do: Some manufacturers offer take-back programs where they will recycle old products for you. This is often the easiest and most responsible way to get rid of your old gadgets.
- Example: If you’re upgrading your smartphone, check if the manufacturer offers a trade-in program. They might recycle your old phone and give you a discount on a new one.
- Donate If Still Usable
- What to Do: If your electronics are still working, consider donating them to charities or schools. They can benefit from the devices, and you’ll keep them out of the landfill.
- Example: Your old laptop could help a local school or community center if it’s still in good working condition. It’s like passing on your old toys to someone who can use them.
- Avoid Throwing in Regular Trash
- What to Do: Never throw electronic gadgets in your regular trash bin. They can end up in landfills where harmful substances can leak into the environment.
- Example: Tossing an old TV into the trash is like throwing hazardous waste directly into the ground. Always choose a proper disposal method.
Why It’s Important
- Protects the Environment: Proper disposal prevents toxic materials from harming our planet, keeping air and water clean.
- Conserves Resources: Recycling and reusing electronic components save resources and reduce the need for new raw materials.
- Promotes Responsible Citizenship: Handling e-waste correctly shows that you care about the environment and are committed to sustainable practices.
Real-World Example
Imagine you have an old laptop that's no longer working. If you just toss it in the trash, it might end up in a landfill where it could leak harmful substances. Instead, you can drop it off at an e-waste recycling center or use a manufacturer’s take-back program. This way, you’re making sure the laptop is properly recycled or reused, helping protect the environment.
By managing e-waste properly, you’re not only keeping your space clutter-free but also contributing to a cleaner, greener planet. It’s all about making responsible choices with your old electronics.
The Information Technology Act, 2000 holds significant importance in India as a pivotal piece of legislation addressing issues related to cybercrime and electronic commerce. This act establishes a legal framework for electronic governance by acknowledging the validity of electronic records and digital signatures. The primary goal of the IT Act 2000 is to facilitate lawful and reliable electronic, digital, and online transactions while also serving as a deterrent against cybercrimes. Encompassing offenses related to computers, computer systems, and networks, the act confers legal validity to electronic contracts and recognizes electronic signatures. The act was enacted to provide legal support to electronic commerce, enable e-governance, and combat cybercrime. IT Act 2000 comprises 13 chapters, 4 schedules, and 94 sections, making it one of the most stringent privacy laws globally.
Overview of the IT Act
- What It Is: The IT Act is a legal framework that governs how technology and the internet are used in India. It aims to promote electronic commerce, enhance cybersecurity, and regulate online activities.
Key Takeaways:
- The Information Technology Act, 2000 is pivotal Indian legislation addressing cybercrime and e-commerce issues.
- The primary goal is to facilitate lawful and reliable digital transactions while deterring cybercrimes. It also aims to enable e-governance.
- The act establishes a legal framework for e-governance by recognizing electronic records and digital signatures. It confers validity on electronic contracts and signatures.
- IT Act 2000 encompasses offenses related to computers, computer systems, and networks.
- It comprises 13 chapters, 4 schedules and 94 sections, making it one of the most stringent privacy laws globally.
 IT Act
IT Act Key Elements of IT Act, 2000
1. Legal Recognition for Electronic Records and Digital Signatures: IT Act, 2000 provides a fundamental legal framework for the acknowledgment and enforceability of electronic records and digital signatures. It goes beyond merely facilitating transactions, it establishes a foundation for the digital realm’s legal infrastructure. According to the legal validity of electronic documents and signatures, the act enables a seamless transition towards electronic governance and commerce, streamlining processes and fostering a more efficient and legally recognized digital environment.
2. Facilitation of Electronic Governance and Commerce: Recognizing the legal validity of electronic records and signatures, IT Act 2000 actively promotes the facilitation of electronic governance and commerce. It extends to electronic delivery of government services, aiming to enhance accessibility and efficiency in public service delivery. Additionally, the act seeks to create a conducive environment for secure and legally recognized transactions between entities, further boosting the growth of e-commerce.
3. Promotion of IT Sector Growth and Innovation: IT Act 2000 goes beyond its role in governance and commerce; it is a key driver in promoting growth within the Information Technology (IT) sector. By providing a comprehensive legal framework for digital technologies, the act encourages innovation and entrepreneurship. It not only safeguards the interests of firms but also stimulates a dynamic and competitive landscape that fosters continuous technological advancements and economic growth within the IT sector.
4. Cybercrime Regulation and Data Protection: The act serves as a critical regulatory tool in addressing the multifaceted challenges posed by digital technology, electronic communication, and cybersecurity. With a specific focus on cybercrime regulation and data protection, IT Act 2000 strives to safeguard digital data and combat cyber threats. It delineates offenses related to computers, computer systems, and networks, offering a legal apparatus to address and mitigate cybersecurity risks in an increasingly interconnected digital landscape.
5. Strict Privacy Laws: IT Act 2000 is acknowledged as one of the world’s strictest privacy laws, going beyond conventional legalities. It extends its jurisdiction to cover offenses related to computers, computer systems, or computer networks. By providing legal validity to electronic contracts and recognizing electronic signatures, the act not only ensures the legal standing of digital transactions but also establishes a robust legal framework for privacy protection in the digital domain. This comprehensive approach underscores the commitment to maintaining the privacy and security of individuals and entities engaging in electronic activities.
Why It Matters
- Promotes Digital Trust: By setting clear rules and protections, the IT Act helps build trust in digital transactions and online interactions.
- Protects Personal and Business Information: It ensures that there are legal measures in place to safeguard sensitive information from unauthorized access and misuse.
- Supports E-Governance: Facilitates digital transactions and governance by providing a legal framework for electronic signatures and documents.
Real-World Example
Imagine you’re shopping online and someone tries to hack your account to steal your credit card information. Thanks to the IT Act, there are legal protections and procedures in place to help you recover your information and hold the hacker accountable. Similarly, if you sign a contract electronically, the act ensures that your digital signature is as valid as a physical one.
Technology and Society: Gender and Disability Issues While Teaching and Using Computers
When we talk about technology and society, it’s crucial to address how gender and disability issues can impact the experience of using and learning with computers. Think of technology as a tool that should be available to everyone equally. However, there are some challenges that different groups might face. Here’s a closer look at these issues:
Gender Issues in Technology
- Gender Gap in Tech: Historically, there’s been a noticeable gap between genders in tech-related fields. Fewer women pursue careers in technology compared to men, which can stem from stereotypes or lack of encouragement.
- Example: If you’re a girl who loves coding but finds that most coding workshops are filled with boys, it might feel discouraging. Encouraging more girls to join and highlighting female role models in tech can help bridge this gap.
- Bias in Software: Sometimes, software and applications might unintentionally reinforce gender biases. For example, voice recognition systems might have difficulty understanding female voices as accurately as male voices.
- Example: If your voice assistant struggles to understand your commands because of its training data, it highlights a need for more inclusive technology design.
Disability Issues in Technology
- Accessibility Challenges: For people with disabilities, using technology can be a challenge if software and hardware aren’t designed with accessibility in mind. This includes issues like not having screen readers for visually impaired users or keyboard-only navigation for those who can’t use a mouse.
- Example: Imagine someone with a visual impairment trying to use a website that doesn’t have text-to-speech options. They might find it difficult to access the information they need.
- Assistive Technologies: Thankfully, there are assistive technologies designed to help. These include screen readers, speech-to-text software, and adaptive keyboards, which can make using computers much easier for people with disabilities.
- Example: A student who uses a wheelchair might use a specialized keyboard that’s positioned within reach, or a visually impaired student might rely on a screen reader to navigate online materials.
Addressing These Issues
- Inclusive Design
- What to Do: Developers should consider various needs when creating technology. This includes ensuring software is usable by people of all genders and abilities.
- Example: Designing a website with both visual and auditory features helps ensure that people with different needs can access the information.
- Encouragement and Support
- What to Do: Providing encouragement and support for underrepresented groups in tech, such as girls and people with disabilities, can help create a more inclusive environment.
- Example: Schools and organizations offering coding workshops specifically for girls or accessible tech training sessions for students with disabilities can make a big difference.
- Awareness and Training
- What to Do: Raising awareness about these issues and providing training for teachers and tech professionals on inclusive practices can help address and reduce these challenges.
- Example: Teachers who are aware of the accessibility features in software can better assist students with disabilities, ensuring they have an equal learning experience.
Why It Matters
- Equity in Education: Ensuring that all students, regardless of gender or disability, have equal access to technology helps promote fairness and inclusivity in education.
- Diverse Perspectives: Including diverse groups in tech creates a richer range of ideas and solutions, benefiting everyone and leading to more innovative technology.
Real-World Example
Imagine a classroom where a computer program is used for learning. If the program is designed with accessibility features, a student with a disability can use it effectively. Meanwhile, if it includes resources that encourage all genders to participate equally in tech activities, it helps break down barriers and fosters a more inclusive environment.
In summary, addressing gender and disability issues in technology ensures that everyone can benefit from and contribute to the digital world. By making technology accessible and inclusive, we help create a more equitable society where everyone has the opportunity to succeed.
Distribution of Marks: CBSE Class 11th Computer Science Unit 3
The distribution of marks for CBSE Class 11th Computer Science Unit 3: Society, Law, and Ethics based on previous year papers generally follows this pattern:
- Society: 2-3 marks
- Law: 2-3 marks
- Ethics: 1-2 marks
- What is a Digital Footprint: 1-2 marks
- Digital Society: 1-2 marks
- Data Protection and Intellectual Property Rights: 2-3 marks
- Open Source Software: 1-2 marks
- Cyber Crime: 2-3 marks
- Malware: 1-2 marks
- E-Waste Management: 1-2 marks
- Information Technology Act (IT Act): 2-3 marks
- Key Elements of IT Act, 2000: 2-3 marks
- Technology and Society: 2-3 marks
Note: This unit typically contributes 20 marks in the Computer Science exam, depending on the specific paper and the emphasis placed on each topic. The distribution may vary slightly each year.
Conclusion
In conclusion, CBSE Class 11th Unit 3: Society, Law, and Ethics offers essential insights into how technology intersects with societal norms, legal frameworks, and ethical considerations. This unit not only prepares students for exams but also equips them with the awareness needed to be responsible digital citizens in today’s tech-driven world. Understanding these concepts is key to navigating the challenges and opportunities that come with our increasingly digital society.
Similar Reads
Class 11th Computer Science Notes
Class 11 Computer Science Complete NotesThese complete Class 11 Computer Science Notes for every unit are tailored to help you easily grasp the essential topics covered in your CBSE Class 11 computer science curriculum. So, whether you are studying for exams, or working on assignments, these notes provide a clear and straightforward guide
7 min read
Class 11 Computer Science Complete NotesThese complete Class 11 Computer Science Notes for every unit are tailored to help you easily grasp the essential topics covered in your CBSE Class 11 computer science curriculum. So, whether you are studying for exams, or working on assignments, these notes provide a clear and straightforward guide
7 min read
Python Notes Class 11 - Computer ScienceIn Python for Class XI, you'll explore the fundamentals of programming with Python, tailored specifically for Class XI students. This article breaks down key concepts such as variables, loops, and functions, making it easy for you to grasp the basics of coding. Whether you're starting from scratch o
15+ min read
CBSE Class 11th Computer Science Unit 3 Notes: Society, Law and EthicsCBSE Class 11th Unit 3: Society, Law, and Ethics is an essential part of the Computer Science curriculum, designed to equip students with the knowledge and awareness needed to navigate our increasingly digital world. CBSE 2024-25 syllabus, this unit goes beyond just theory—it dives into the real-wor
15+ min read
CBSE Class 11 Syllabus 2024-25 CBSE Class 11 Syllabus for the academic year 2023-24. This Class 11 Syllabus has been designed to provide students with a strong foundation for higher studies as it covers major subjects such as Mathematics, Science, Social Science, Languages, and Skill-Based subjects. In this guide, we will provide
15+ min read
CBSE Class 11 Study Material and Notes PDF 2024 CBSE Class 11 is an important phase for students because it sets the base for all important topics that will be covered in the next class. It is important to study sincerely in Class 11 not only to score high marks but also to prepare for competitive exams. Students should utilize the Class 11 acade
3 min read
CBSE Class 11 Maths Notes CBSE Class 11 Maths Revision Notes have been designed in the most basic and detailed format possible, covering nearly all domains such as differential calculus, arithmetic, trigonometry, and coordinate geometry. We know how hard it gets when you shift to an altogether new grade where subjects are no
15+ min read
CBSE Class 11 Physics Notes CBSE Class 11 Physics Notes 2023-24 is a comprehensive guide for CBSE Class 11 students. The class 11 syllabus is designed to provide students with a strong foundation in the basic principles of physics, including Measurement, Vectors, Kinematics, Dynamics, Rotational Motion, Laws of Motion, and Gra
12 min read
CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Notes CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Notes: Achieving success in CBSE exams requires a clear understanding of Chemistry concepts. Thus, Class 11 students must obtain well-structured Chemistry Class 11 Notes from experienced teachers. This comprehensive set of notes is designed to help students understand the fun
10 min read
CBSE Class 11 Chapter-Wise Notes Biology CBSE Class 11 Chapter-wise Notes Biology covered topics that are essential for the preparation of exams and carry significant weight for competitive exams. Class 11 Biology is an interesting subject that covers a range of various issues such as The Living World, Anatomy Kingdom, Structural Organizat
4 min read
CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Notes Business Studies is the area of study that talks about the principles of business, economics and management. GeeksforGeeks Class 11 Business Studies Notes have been designed according to the CBSE Syllabus for Class 11. These revision notes consist of detailed Chapterwise important topics and concept
9 min read
CBSE Class 11 Microeconomics Notes Microeconomics is the study of households', individuals', and firms' behaviour towards the allocation of resources and the decision-making process. In short, it deals with the choices made by people and the factors affecting their choices. GeeksforGeeks Class 11 Microeconomics Notes have been design
7 min read
CBSE Class 11 Statistics for Economics Notes Economic statistics is a topic in applied statistics that concerns the collection, organization, and presentation of data. GeeksforGeeks Class 11 Statistics for Economics Notes have been designed according to the CBSE Syllabus for Class 11. These revision notes consist of detailed Chapterwise import
8 min read