Type conversion happens when we assign the value of one data type to another. If the data types are compatible, then C# does Automatic Type Conversion. If not comparable, then they need to be converted explicitly which is known as Explicit Type conversion.
Type Casting can be divided into two parts as mentioned below:
- Implicit Type Conversion (Type Safe)
- Explicit Type Conversion (Manual Conversion)
1. Implicit Type Casting
In C# Implicit Type Casting also known as Automatic type conversion refers to the built-in mechanisms that control the flow of execution in your program without explicitly using timers or scheduling objects. These mechanisms are inherent to the language and the underlying runtime environment.
Conditions of Implicit Type Casting
- The two data types are compatible.
- When we assign the value of a smaller data type to a bigger data type.
The implicit type casting is done automatically when we try to convert small data into large data types.
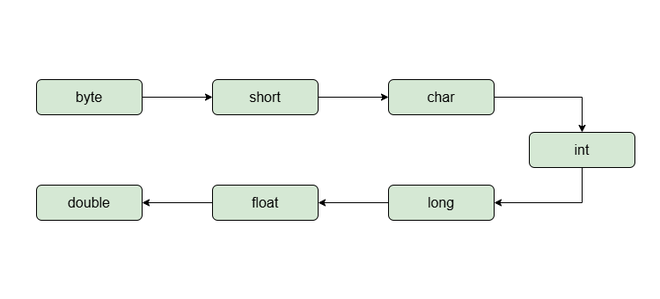
In C#, the numeric data types are compatible with each other but no automatic conversion is supported from numeric type to char or boolean. Also, char and boolean are not compatible with each other. Before converting, the compiler first checks the compatibility accordingly
Example 1:
C# // Demonstrating Implicit Type Conversion using System; namespace Casting { class Geeks { // Main Method public static void Main(String[] args) { int i = 57; // automatic type conversion long l = i; // automatic type conversion float f = l; Console.WriteLine("Int value :" + i); Console.WriteLine("Long value :" + l); Console.WriteLine("Float value :" + f); } } } OutputInt value 57 Long value 57 Float value 57
Example 2: This program gives a compilation error because we try to convert a large data type into a small type
C# // Incompatible Data Conversion using System; namespace Casting { class Geeks { // Main Method public static void Main(String[] args) { double d = 765.12; // Incompatible Data Type int i = d; // Display Result Console.WriteLine("Value of i is :", +i); } } } Output:
main.cs(13,17): error CS0266: Cannot implicitly convert type `double' to `int'. An explicit conversion exists (are you missing a cast?)
Compilation failed: 1 error(s), 0 warnings
Note: If we want to assign a value of larger data type to a smaller data type we perform explicit type casting. It may result into the lossy conversion.
Implicit is not the Solution for such kind of problem where we want to convert a large data type into a small type. So, let check on how we can do this.
2. Explicit Type Casting
Explicit type casting is the process of converting a value of one data type to another data type that is not implicitly compatible. This is necessary when there’s a potential for data loss or when the compiler cannot implicitly perform the conversion. When we try to assign a double value to the int data type it leads to a compilation error when types are not compatible with each other
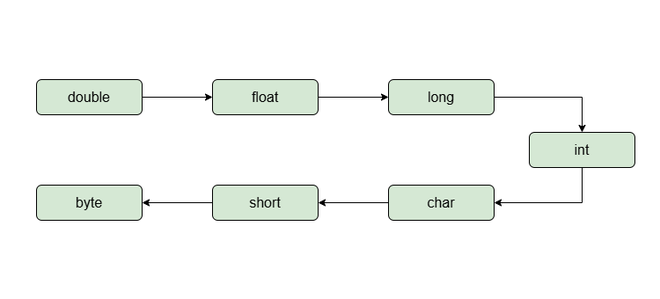
Example 1: Using Explicit Conversion to convert double into int.
C# // Demonstration of Explicit Type Conversion using System; namespace Casting { class Geeks { // Main Method public static void Main(String[] args) { double d = 765.12; // Explicit Type Casting // larger data into smaller data type int i = (int)d; // Display Result Console.WriteLine("Value of i is " + i); // the value of i becomes 765 and there is a loss of // 0.12 value. } } } This solves our some of the problems, but we can also have some available methods that can help us for conversion mentioned below.
Type Conversion Methods
There are some built in methods defined for type conversions mentioned below:
Method | Descryption |
|---|
ToBoolean | It will converts a type to Boolean value |
ToChar | It will converts a type to a character value |
ToByte | It will converts a value to Byte Value |
ToDecimal | It will converts a value to Decimal point value |
ToDouble | It will converts a type to double data type |
ToInt16 | It will converts a type to 16-bit integer |
ToInt32 | It will converts a type to 32 bit integer |
ToInt64 | It will converts a type to 64 bit integer |
ToString | It will converts a given type to string |
ToUInt16 | It will converts a type to unsigned 16 bit integer |
ToUInt32 | It will converts a type to unsigned 32 bit integer |
ToUInt64 | It will converts a type to unsigned 64 bit integer |
Example: Typecasting using built-in methods
C# // Using Built In Type Conversion Methods using System; namespace Casting { class Geeks { // Main Method public static void Main(String[] args) { int i = 12; double d = 765.12; float f = 56.123F; // Using Built- In Type Conversion // Methods & Displaying Result Console.WriteLine(Convert.ToString(f)); Console.WriteLine(Convert.ToInt32(d)); Console.WriteLine(Convert.ToUInt32(f)); Console.WriteLine(Convert.ToDouble(i)); Console.WriteLine("GeeksforGeeks"); } } } Output56.123 765 56 12 GeeksforGeeks
Similar Reads
C# Data Types
Data types specify the type of data that a valid C# variable can hold. C# is a strongly typed programming language because in C# each type of data (such as integer, character, float, and so forth) is predefined as part of the programming language and all constants or variables defined for a given pr
7 min read
C# | Type.Equals() Method
Type.Equals() Method is used to check whether the underlying system type of the current Type is the same as the underlying system type of the specified Object or Type. There are 2 methods in the overload list of this method as follows: Equals(Type) Method Equals(Object) Method Type.Equals(Type) Meth
4 min read
C# - Char Struct
In C#, the Char struct is used to represent a single Unicode character as a UTF-16 code unit, defined under the System namespace. A Char in C# is a 16-bit value, and it can represent characters in the Basic Multilingual Plane (BMP). Characters beyond 0xFFFF are represented by surrogate pairs (two Ch
4 min read
C# | How to get TypeCode for the class String
GetTypeCode() method is used to get the TypeCode of the specified string. Here TypeCode enum represents a specific type of object. In TypeCode every data type is represented by a specific number like String is represented by 18, Int32 is represented by 9, etc. Syntax: public TypeCode GetTypeCode ();
2 min read
C# | Char.ToString() Method
In C#, Char.ToString() is a System.Char struct method which is used to convert the value of this instance to its equivalent string representation. This method can be overloaded by passing different type of arguments to it. Char.ToString(IFormatProvider) Method Char.ToString(Char) Method Char.ToStrin
2 min read
C# | Object Class
The Object class is the base class for all the classes in the .Net Framework. It is present in the System namespace. In C#, the .NET Base Class Library(BCL) has a language-specific alias which is Object class with the fully qualified name as System.Object. Every class in C# is directly or indirectly
4 min read
C# UInt32 Struct
In C#, the UInt32 struct represents a 32-bit unsigned integer (commonly referred to as the uint data type). It is defined in the System namespace and provides various methods for mathematical computations, parsing, and type conversion. Because of it is an unsigned type, it only holds non-negative va
2 min read
C# Convert Class
Convert class in C# provides different methods to convert a base data type to another base data type. The base types supported by the Convert class are Boolean, Char, SByte, Byte, Int16, Int32, Int64, UInt16, UInt32, UInt64, Single, Double, Decimal, DateTime, and String. It also provides methods tha
4 min read
C# UInt16 Struct
In C#, the UInt16 struct, defined under the System namespace, represents a 16-bit unsigned integer, commonly referred to as the ushort data type. It does not support negative values and provides a range from 0 to 65,535. The UInt16 struct inherits the ValueType class, which further inherits the Obje
2 min read
C# | Type.HasElementTypeImpl() Method
Type.HasElementTypeImpl() Method is used when overridden in a derived class, implementing the HasElementType property and determines whether the current Type encompasses or refers to another type. It means this method checks whether the current Type is an array, a pointer, or is passed by reference.
3 min read