Evolution Notes for Class 12 Chapter 6
Last Updated : 05 Apr, 2024
Evolutionary biology is the study of the evolutionary processes that produced the diversity of life on Earth. Earth came into existence sometime between 4 and 5 billion years ago. Life evolved on planet Earth about 3.5 billion years ago. Since then, approximately 15 million different species of organisms have evolved. But only about two million have been identified so far. In this article, we will discuss how the life of these, at first originated on earth and how such a vast variety of organisms evolved through variation and natural selection.
Origin of Life
The origin of life is considered a unique event in the history of the universe. Several theories have been put forth to explain the origin of life.
- Big Bang Theory: The universe is vast. Huge clusters of galaxies comprise the universe. The Big Bang theory attempts to explain to us the origin of the universe and the creation of life. Developed in 1927, it is considered the most credible scientific explanation of how the universe was created. It suggests that through a process of expansion and explosion, hydrogen gas was created which led to the formation of stars, and their death (supernova) led to the creation of life.
- Panspermia Theory: The panspermia hypothesis states that the seeds of life exist all over the universe and can be propagated through space from one location to another. For millennia, this idea has been a topic of philosophical debate. However, due to the lack of any validation, it remained merely speculative until a few decades ago.
- Theory of Spontaneous Generation: The theory of spontaneous generation believed that life originated spontaneously from non-living decaying and rotting matter like straw and mud. This theory was disproved by Louis Pasteur. Louis Pasteur demonstrated that life comes from pre-existing life. He showed that in pre-sterilized flasks, life did not come from killed yeast while in another flask open to air, new living organisms arose from ‘killed yeast’.
- Chemosynthetic Theory of Life: It was proposed by A.I. Oparin of Russia and Haldane of England. They proposed that the first form of life could have come from pre-existing non-living organic molecules, e.g. RNA, protein, etc., and that the formation of life was preceded by chemical evolution, i.e., the formation of diverse organic molecules from inorganic constituents. The conditions on earth were – high temperature, volcanic storms, and reducing atmosphere containing CH4, NH3, etc.

It was supported by S.L. Miller, an American scientist. In 1953, he created similar conditions on a laboratory scale. He created electric discharge in a closed flask containing Methane (CH4), Hydrogen (H2), Ammonia (NH3), and Water vapor (H2O) at 8000C. He observed the formation of amino acids. Miller's experiment showed how simple molecules could be assembled into the more complex molecules necessary for life by natural processes.
Also Read: Abiogenesis
The formation of complex organisms through ‘gradual change’ from simple ancestral types over the course of geological time is termed Evolution.
The theory of evolution is a shortened form of the term “theory of evolution by natural selection,” which was proposed by Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace in the nineteenth century. Darwin and a scientific contemporary of his, Alfred Russel Wallace, proposed that evolution occurs because of a phenomenon called natural selection. In the theory of natural selection, organisms produce more offspring than are able to survive in their environment.
Those that are better physically equipped to survive, grow to maturity, and reproduce. Those that are lacking in such fitness, on the other hand, either do not reach an age when they can reproduce or produce fewer offspring than their counterparts. Natural selection is sometimes summed up as “survival of the fittest” because the “fittest” organisms are the ones that reproduce most successfully, and are most likely to pass on their traits to the next generation. Natural selection was such a powerful idea in explaining the evolution of life that it became established as a scientific theory.
Evidence for Evolution
The evidence supporting organic evolution is derived from a number of fields of Biology. Those discussed here are:
- Palaeontological evidence: Different-aged rock sediments contain fossils of different life forms that probably died during the formation of the particular sediment. Some of them appear similar to modern organisms. They represent extinct organisms, e.g., Dinosaurs. A study of fossils in different sedimentary layers indicates the geological period in which they existed. Hence, new forms of life have arisen at different times in the history of Earth.
- Embryological evidence: It was proposed by Ernst Heckel based on the observation of certain features during the embryonic stage common to all vertebrates that are absent in adults. For example, the embryos of all vertebrates including humans develop a row of vestigial gill slits just behind the head but it is a functional organ only in fish and not found in any other adult vertebrates.
- Morphological evidence: Though organisms of different species and groups are quite different from each other, they still retain certain common features. Morphological evidence for evolution is derived from:
- Divergent evolution: Species from a common ancestral origin evolve similar anatomical parts (called homologous structures) but with dissimilar functions. For example, whales, bats, cheetahs, and humans (all mammals) share similarities in the pattern of bones of forelimbs.
- Convergent evolution: It creates analogous structures that have similar forms or functions but were not present in the last common ancestor of those groups. Both sharks and dolphins have similar body forms, yet are only distantly related: sharks are fish and dolphins are mammals.
- Molecular evidence: Similarities in proteins and genes performing a given function among diverse organisms give clues to common ancestry. These biochemical similarities point to the same shared ancestry as structural similarities among diverse organisms.
Also Read: Fossils - Tracing Evolutionary Relationships
Adaptive Radiation
Adaptive radiation is a rapid increase in the number of species with a common ancestor, characterized by great ecological and morphological diversity. This process occurs due to natural selection.
An example of adaptive radiation is Darwin finches, found on Galapagos Island. A large variety of finches is present in Galapagos Island that arose from a single species, which reached this land accidentally. As a result, many new species have evolved, diverged, and adapted to occupy new habitats. These finches have developed different eating habits and different types of beaks to suit their feeding habits. The insectivorous, blood-sucking, and other species of finches with varied dietary habits have evolved from a single seed-eating finch ancestor.
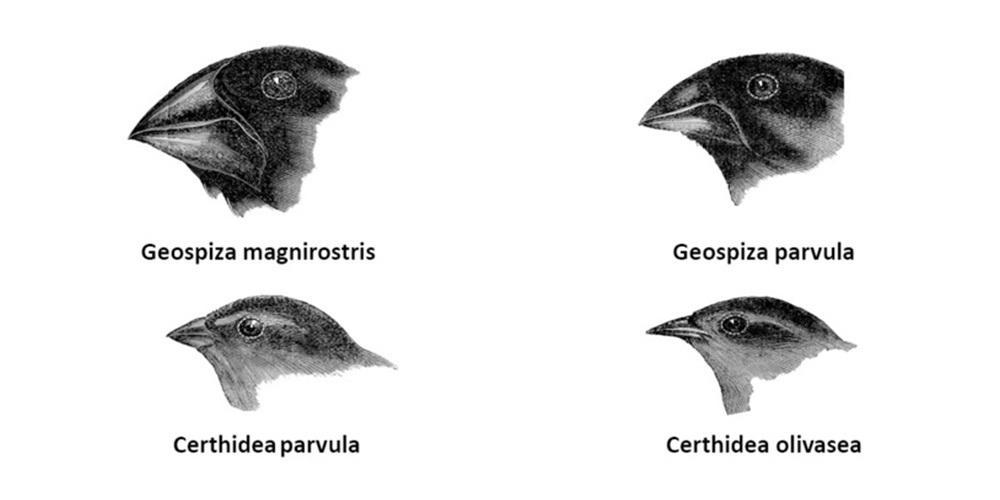
Biological Evolution
Branching descent and natural selection are the two key concepts of the Darwinian Theory of Evolution.
- Branching descent is the process of the development of a new species from a single common descendant. New species developed and become geographically adapted to a new environment. This results in reproductive isolation and finally to the development of a new species.
- Natural Selection is the process through which populations of living organisms adapt and change. Individuals in a population are naturally variable, meaning that they are all different in some ways. This variation means that some individuals have traits better suited to the environment than others.
Darwin asserted that variations, which are heritable and which make resource utilization better for few will enable only those to reproduce and leave more progeny. Hence for a period of time, over many generations, survivors will leave more progeny and there would be a change in population characteristics and hence new forms appear to arise.
Mechanism of Evolution
Various theories about the mechanism of evolution have been proposed; some of them such as Lamarck’s theory of “Inheritance of acquired characters” and De Vries’ theory of ‘mutation’ are now of historical importance only. Darwin’s theory of Natural selection still holds ground but was modified with progress in genetics and developed into the Modern synthetic theory which is regarded as the most valid theory of evolution.
Darwin talked about variation but did not know about the sources of variation. With progress in genetics, the sources of variation were discovered and Darwin’s original theory of Natural Selection was modified. This new theory was termed Neo-Darwinism or Modern Synthetic Theory.
Hardy-Weinberg Principle
Hardy–Weinberg Principle mathematically explains the occurrence and consistency of gene frequency for a particular gene. The principle states that the allelic frequency remains constant through generations and the gene pool remains constant. This can be mathematically represented as:
(p+q)2 =1 or p2 +2pq+q2 =1
Factors affecting the Hardy-Weinberg principle:
- Mutation
- Genetic drift
- Natural selection
- Genetic recombination
- Gene flow
All these factors contribute to the change in gene frequency of a species in an area. If a few individuals from a species migrate to another place, the gene frequency changes again. It decreases from the place from where the individuals migrate and increase in the place they migrate to. If the frequency of the genes is high enough in the newly migrated land to start a new species, the migrated individuals become the founder species, and the effect is called the Founder effect. Thus, all these mechanisms contribute to the process of evolution.
Brief Account of Evolution
Evolution refers to the gradual change which occurs in an organism over a long duration of time. It is a slow-going process that results in the development of the organism. Life originated on Earth about 3.5 billion years ago. It is believed that there might have been the presence of simple elements on earth which may have given rise to simple organic and inorganic molecules. From these simple molecules, complex molecules like protein, DNA, etc. may have been formed.
Other evolutionary changes may have resulted in the formation of simple cells and the result of the continuous evolution on Earth is the several species of plants and animals that exist on Earth. Today, the diversity on earth varies from unicellular amoeba to a human beings and from unicellular Algae like Chlorella to a huge banyan tree.
Origin and Evolution of Man
Man belongs to the family Hominidae of the order Primates. Humanlike apes belong to the same order. With the passage of time, their ancestors evolved and became more and more different. The first-ever ancestors of humans are believed to have originated in Africa, eventually migrating to Europe, Asia, and the rest of the world. Man originated through several stages:
- Dryopethicus: It is the earliest known ancestor of man. They were found in some parts of Africa, Asia, and Europe. The evolution of man began with him. Dryopethicus was followed by Australopithecus.
- Australopithecus: These were 1.2 meters tall and could walk upright. They inhabited the African mainland. They had large jaws and human-like teeth.
- Homo habilis: They were five feet tall and could make use of tools. They are believed to have been able to speak.
- Homo erectus: They were more evolved beings. They were also upright and had a larger brain size. They had a prominent speech. They invented fire and were carnivorous.
- Neanderthals: Homo sapiens is the only extant species of hominin around today, but a few thousand years ago, there were a few other species that existed alongside anatomically modern humans – the Neanderthals, Denisovans and the Homo floresiensis. Today, scientists consider Neanderthals to be more of a subspecies of humans rather than a completely separate species.
- Homo sapiens: These are modern men. They developed the power of thinking, used tools, were omnivorous, and produced art. Their brain size was reduced to 1300 cc.

CBSE Previous Year Question Papers
Learn from CBSE Previous Year Question Papers to boost your understanding and excel in your studies.
Also Read:
Similar Reads
CBSE Class 12 Biology Syllabus NCERT Class 12 Biology Syllabus: NCERT Class 12 Biology Syllabus covers important topics that provide students with a comprehensive understanding of living organisms, their structure, function, and behavior. These notes introduce fundamental concepts of biology including Sexual reproduction in Flowe
4 min read
CBSE Class 12 Biology Notes CBSE Class 12 Chapter-wise Notes Biology helps students to score well in their board examinations. Class 12 Biology is a subject that comes with a wide range of topics, which include inheritance, evolution, reproduction, human health and disease, biotechnology, Ecosystem, and Biodiversity and Conser
4 min read
Chapter 1: Sexual Reproduction In Flowering Plants
Parts of a Flower and Their FunctionsA flower is the reproductive structure of angiosperm that facilitates sexual reproduction. The 4 main parts of the flower include - sepals, petals, stamens (male parts of the flower), and carpels (female part of the flower). The different parts of the flower have their unique function. The primary f
9 min read
Pollen Grains​Pollen grains are minute structures of varying size and shape that contain the androecium, the male reproductive organ of a flower. Pollen grains are also called microgametophytes. The formation of pollen grains occurs through the process of microsporogenesis and consists of a protective outer laye
5 min read
The Structure and Functions of PistilIn flowering plants, sexual reproduction is a complex process that involves the mating of male and female gametes to create seeds for the following generation. The pistil, which is located in the centre of the flower, is the female reproductive structure in flowering plants. What is Pistil?A pistil
4 min read
PollinationPollination is the biological process by which pollen from the male part of the flower transfers to the female part of the same or on different flowers. Pollination results in fertilization and the production of seeds. Pollination is important for the reproduction of plants. Pollination can occur in
6 min read
Double Fertilization: Process & SignificanceDouble fertilization is a unique reproductive process that occurs in flowering plants (angiosperms). Unlike in most other organisms where a single sperm fertilizes an egg, in double fertilization, one male gamete fertilizes the egg cell to form the embryo, while another male gamete fuses with two po
8 min read
Post FertilizationPost-fertilization events are the processes that occur after the fusion of the male and female gametes during sexual reproduction. These post-fertilization events in flowering plants are crucial for the development of the zygote into a mature seed or fruit. Understanding post-fertilization events in
6 min read
Apomixis and Polyembryony: Differences, Types, SignificanceApomixis and polyembryony are two different but related biological processes that result in the production of offspring without fertilization. Apomixis is a type of asexual reproduction where seeds are produced without gametic fusion. While polyembryony is a process in which multiple embryos are pro
5 min read
Chapter 2: Human Reproduction
NCERT Notes on Human Reproduction Class 12 Chapter 2NCERT Notes of Class 12 Chapter 2 Human Reproduction: Human reproduction is the biological process by which a new individual offspring is produced from one or two parent organisms. The Human Reproduction process involves the fusion of gametes, which are specialized cells that carry genetic informati
15+ min read
Gametogenesis - Spermatogenesis and OogenesisGametogenesis is a process of producing male and female gametes, carried out by all sexually reproducing organisms. The process involves various multiple stages of division and differentiation and is highly regulated under hormonal control. GametogenesisGametogenesis produces male and female gametes
4 min read
Menstrual CycleIn a day-to-day existence cycle, a lady's body is powerless against different changes. The pattern of these progressions happens in ladies consistently, emphatically for pregnancy is known as the feminine cycle. At the point when an ovum is unfertilized, the uterus lining sheds and prompts a dischar
9 min read
Fertilizations And ImplantationFertilization and implantation are the 2 important events in human reproduction, which is the biological process of producing new individuals from a union of male and female gametes. This complex process involves the fusion of gametes, the development of a zygote, and the growth and differentiation
5 min read
Embryo Development - Development Process of FetusBirth gives process to a child is known as reproduction. A species' survival depends on its ability to reproduce. There are two different ways to reproduce: Sexual reproduction is asexual reproduction. Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that occurs without the involvement of 2 parents. A
5 min read
Parturition And Lactation - Biology Notes Class 12Parturition And Lactation: Several intricate physiological processes, such as fertilisation, implantation, gestation, and delivery, are involved in human reproduction. The act of giving birth, often referred to as parturition, is a significant occasion that signals the conclusion of pregnancy and th
4 min read
Chapter 3: Reproductive Health
Notes on NCERT for Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Reproductive HealthNotes on NCERT for Class 12 Biology Chapter 3 Reproductive Health: Reproductive health simply means people in a society living with physically and functionally normal reproductive organs and normal behavioral and emotional responses toward sex-related matters. According to WHO “reproductive health m
10 min read
Population Stabilization And Birth Control - Class 12Population Stabilization And Birth Control: Reproductive Health means total well-being in all aspects of reproduction, i.e., physical, emotional, behavioral, and social. Counseling and raising awareness among people about reproductive organs, adolescence, and associated changes, safe and hygienic se
6 min read
Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP)Medical termination of Pregnancy (MTP) is an intentional or voluntary termination of pregnancy before its full term. Before the 1960s, surgical methods like vacuum aspiration or dilatation and curettage were common, but medication has since emerged as an alternative option. Medical Termination of Pr
5 min read
Chapter 4: Principles Of Inheritance And Variation
Principles of Inheritance and Variation CBSE Notes for Chapter 4Inheritance is the term given to the process by which characters are passed from parents to offspring which forms the basis of heredity. Heredity is the process of passing down genetic traits from parents to offspring. The degree of difference in characters between a parent and offspring is called v
15 min read
Mendel's Laws of Inheritance | Mendel's ExperimentsMendel's law of inheritance states that offspring inherited from their parents that results in similar characteristics of parents and offspring. This law of inheritance depends upon three other laws including the law of dominance, the law of segregation, law of independent assortment. Gregor Mendel
8 min read
Inheritance of One Gene NotesWe never wonder why Lion can give birth to Lions only, or why a bird can reproduce in the same species and no other species. Not everything is possible, Isn't it? Also, No human being look exactly identical, even with twins there are differences in every individual. Some siblings look similar while
6 min read
Chromosomal Theory of InheritanceThe essential idea behind the chromosomal theory of inheritance is that genes are located on chromosomes and that the behavior of chromosomes during meiosis and fertilization provides the basis for inheritance patterns. In the early 1900s, pioneering geneticists Walter Sutton and Theodor Boveri form
6 min read
Linkage And Recombination - Principles Of Inheritance And Variation Class 12 NCERTCBSE Class 12- Principles Of Inheritance And Variation- Linkage And Recombination: Linkage and recombination are the phenomena that describe the inheritance of genes. Linkage and Recombination both are related to the genetic information inherited from parents to offspring. Linkage is the tendency of
6 min read
What is Polygenic Inheritance?Polygenic inheritance is a type of inheritance in which multiple genes control the phenotype of an organism. The phenotypes or traits can be height, skin color, the color of the eyes, etc. This type of inheritance is also known as quantitative inheritance or multifactorial inheritance. Such traits a
7 min read
MutationThe human body might be visualized as a simple organism. But it is the combination of different complex processes. From the outside, a human body might resemble a very simple one. A body that has two arms, two legs & one head for monitoring purposes. But from the inside of the body, there are ma
15+ min read
Chromosomal Disorders: Principles of Inheritance And Variation Class12CBSE Class-12 Principles Of Inheritance And Variation - Chromosomal Disorders: The chromosomes are thread-like structures that are mainly present in the nucleus which carries the hereditary information of genes that are passed from the parents to the offspring. Due to some irregularities of cell div
5 min read
Chapter 5: Molecular Basis Of Inheritance
Evolution Notes for Class 12 Chapter 6Evolutionary biology is the study of the evolutionary processes that produced the diversity of life on Earth. Earth came into existence sometime between 4 and 5 billion years ago. Life evolved on planet Earth about 3.5 billion years ago. Since then, approximately 15 million different species of orga
11 min read
Molecular Basis of Inheritance Notes Class 12CBSE Class 12 Molecular Basis of Inheritance: Inheritance is transmitted by certain molecules that Mendel termed as ‘factors’, but their nature was discovered later with the development of various scientific techniques. The molecules which govern the inheritance are called genes and it is of two typ
15+ min read
DNA: Structure, Types, and FunctionsDNA structure is made of nucleotide base pairs (other than RNA). DNA is the hereditary material that is possessed by all the organisms found on the Earth except certain virus species. DNA functions involve the transfer of genetic information from generation to generation. The full form of DNA is Deo
11 min read
Packaging of DNA Helix: Histones & ImportanceDNA packaging refers to the process through which DNA molecules are tightly compacted into a smaller volume so that they can fit into the nucleus of a cell. DNA packaging is important because the length of DNA molecules is much greater than the size of the cell nucleus, and therefore, if the DNA wer
5 min read
Search For Genetic MaterialThe search for genetic material has been important in understanding inheritance and evolution. Scientists have explored various models and experiments to identify the substance responsible for transmitting hereditary traits. From Griffith's transformation experiments to Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty's
5 min read
Difference Between DNA and RNAThe difference Between DNA and RNA lies in their structure, function, and location within cells, with DNA typically double-stranded, storing genetic information in the nucleus, while RNA is generally single-stranded, involved in protein synthesis, and present in various cellular compartments. DNA (D
6 min read
RNA - Definition, Structure, Types and FunctionsRNA is a ribonucleic acid that helps in the synthesis of proteins in our body. This nucleic acid is responsible for the production of new cells in the human body. It is usually obtained from the DNA molecule. RNA resembles the same that of DNA, the only difference being that it has a single strand u
11 min read
DNA ReplicationDNA replication is a fundamental biological process by which a cell duplicates its entire DNA. DNA is a self-replicating structure and the replication is catalyzed by enzymes. Through DNA Replication, genetic information is passed on from one generation of cells to the next during cell division. It
8 min read
The Experimental Proof Of DNA ReplicationThe process by which cells duplicate their genetic material during cell division—the replication of DNA—was still largely a mystery. This sparked a race to understand how DNA replication happens among several well-known experts. The experimental evidence of DNA replication, which showed that DNA rep
5 min read
Transcription of DNATranscription of DNA is a cellular process where the genetic information encoded in DNA is converted into RNA. It initiates with RNA polymerase binding to the DNA at a specific promoter region. Then, the enzyme unwinds the DNA and synthesizes a complementary RNA strand by following the DNA template.
6 min read
Genetic Code - Molecular Basis of InheritanceCBSE Class12- Molecular Basis Of Inheritance- Genetic Code: The sequence of nucleotides in deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid which determines the amino acids sequence of proteins is known as Genetic code. DNA consists of information for protein sequences. RNA consists of four nucleotides: a
5 min read
Genetic Code and MutationsGenetic code and mutations are important to understand and explain the central dogma of biology. The set of rules governing how DNA sequences are translated into proteins is the genetic code. The four nucleotide bases adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C), which are organized in pa
5 min read
tRNA - the Adapter MoleculetRNA is also known as transfer RNA is a subtype of RNA, tRNA help in the protein synthesis process. tRNA carries the amino acid to the ribosome, which is the molecular machine that assembles the protein, and ensures that the amino acid is incorporated into the growing protein chain in the correct or
5 min read
RNA TranslationThe Central Dogma, claims that once "information" has transferred into protein, it cannot be retrieved. In greater detail, information transmission from nucleic acid to the nucleic acid or nucleic acid to protein may be conceivable, but transfer from protein to protein or protein to nucleic acid is
15+ min read
Lac OperonLac operon consists of the genes that are required for the metabolism of lactose in a bacterium E. coli and some other enteric bacteria. The name Lac operon actually stands for lactose operon. Lac operon works only when the nutrient source lacks glucose and has only lactose as it takes more steps to
7 min read
Human Genome ProjectHuman Genome Project was the world’s largest collaborative biological project that gave us the ability to examine the full genetic manual for creating a human being in nature. HGP was international scientific research that mainly aims to determine the base pairs that make human DNA, as well as the i
9 min read
What is DNA Fingerprinting?DNA Fingerprinting is a technique used to identify individuals by analyzing their unique DNA patterns. Studying the DNA Fingerprinting steps and process helps in understanding genetic relationships, solving crimes, and identifying individuals based on their unique DNA profiles. In this article, we w
10 min read
Chapter 6: Evolution
Origin of LifeThe origin of life on earth is one of the mysteries to mankind. According to a common man, life is gifted by god whereas scientists believe that life has originated from non-living matter by natural means. This mystery of whether life originated from non-living matter was solved by scientists Pirie.
4 min read
Evolution Of Life Forms – A TheoryEvolution is a process of gradual changes in the heritable characteristics of a biological population, over successive generations, over a long period. (Population: - It is a group of individuals of the same species who live in the same area and can interbreed) Theories of EvolutionTill now, several
5 min read
Understanding Adaptive Radiation: Evolutionary Diversification ExplainedAdaptive radiation is a phenomenon observed in evolutionary biology, that involves the rapid diversification of species into various forms to exploit new ecological niches. This process leads to the exposure of multiple species with distinct adaptations, enhancing their survival in diverse environme
4 min read
Hardy-Weinberg PrincipleA system of guidelines for genetic inheritance is known as mendelian inheritance. A monk by the name of Gregor Mendel made the initial discoveries of genetics in the 1850s, and his findings were first published in 1866. People have been aware of how qualities are passed on from parents to their offs
13 min read
Evolution Of Humans - History, Stages, Characteristics, FAQsHumans, or Homo sapiens, are a species of upright-walking beings known for their cultural diversity, inhabiting the Earth's surface. Believed to have originated in Africa around 315,000 years ago, human evolution is a complex process involving the development of traits such as bipedalism and languag
6 min read
Chapter 7: Human Health and Disease
NCERT Notes on Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 - Human Health and DiseaseNCERT Chapter 7 of Class 12 Notes on Human Health and Disease: According to the World Health Organisation, health can be defined as a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease and infirmity. Good health has many benefits like it helps to keep us
15+ min read
Common Diseases In HumansDisease: - A disease is a physiological condition in which the human body fights against the external or internal causes of infection. On the basis of externally caused diseases, various examples are present, ranging from bacteria, viruses, protozoans, helminths, and many more. Pathogen: - The patho
5 min read
Immunity - Definition, Types and VaccinationImmunity is a defense mechanism of the body that is provided by the immune system and helps in fighting disease-causing organisms. There are two immunity types: innate and acquired immunity. Immunity-enhancing foods help boost the body's immune system Vaccination also enhances immunity by exposing t
11 min read
Innate And Acquired ImmunityThe immune system fights against germs and foreign substances on the skin, in the body's tissues, and in bodily fluids such as blood. The overall ability of the host to fight the disease-causing organisms conferred by the immune system is called Immunity. The immune system can be broadly categorized
5 min read
Importance of Vaccines, Vaccination and ImmunizationVaccination and immunization play a crucial role in protecting individuals and communities from infectious diseases. They help to stimulate the immune system and prepare it to recognize and fight off specific pathogens. Vaccination classes 6 and 12 are important topics frequently asked in examinatio
7 min read
Alcohol and Drug Abuse Prevention ControlAs opposed to the normal thoughts pervasive in general society, substance use is very far-reaching. So is substance misuse. It's anything but a little issue, confined to the domain of the feeble and detestable. The utilization of medications rises above race, orientation, age, or financial status. T
10 min read
Chapter 8: Microbes In Human Welfare
Microbes in Human Welfare NotesCBSE Class 12 Chapter 8 Microbes in Huaman Welfare: Microbes are the smallest living organisms that can only be seen under the microscope. Microbes are found everywhere. Examples- are air, water, soil, inside and outside the bodies of plants and animals, thermal vents (1000 degree Celsius), under th
6 min read
Microbes In Human WelfareMicrobes are microscopic organisms, that can be classified under protozoa, bacteria, fungi, and microscopic plants viruses, viroid, and prions (proteinaceous infectious agents). They are present everywhere– in soil, water, and air, inside our bodies, animals, and plants. Not only in life forms, but
6 min read
BiofertilizersBiofertilizers are biologically active substances that help in enriching the soil's fertility. Biofertilizers are microbes or microbial products. It helps to reduce the use of chemical fertilizers. Reducing the use of chemical fertilizers from the environment biofertilizers helps to protect the ecos
8 min read