How to get average velocity ?
Last Updated : 03 Apr, 2025
When an object moves, its position changes over time. But have you ever wondered how quickly it changes its position or in which direction? To describe this, we use the concept of average velocity. Here, we will explore and understand average velocity.
What is Average Velocity?
Average velocity is a vector quantity, defined as the change in position or displacement (∆x) divided by the time interval (∆t) during which the displacement occurs. The average velocity can be positive or negative, depending on the sign of the displacement. Its SI unit is meters per second (m/s or ms⁻¹).
How to find Average Velocity?
To calculate the average velocity, we divide the total displacement by the total time elapsed, as shown below:
ΔV = Δx/ Δt
where, ΔV is the average velocity, Δx is the displacement, and Δt is the total time. If the starting time is zero, the formula simplifies to:
ΔV = xf−x0 / tf
where, xf is the final position, x0 is the initial position, and tf is the final time.
Average velocity in a distance-time graph is shown by the graph below:
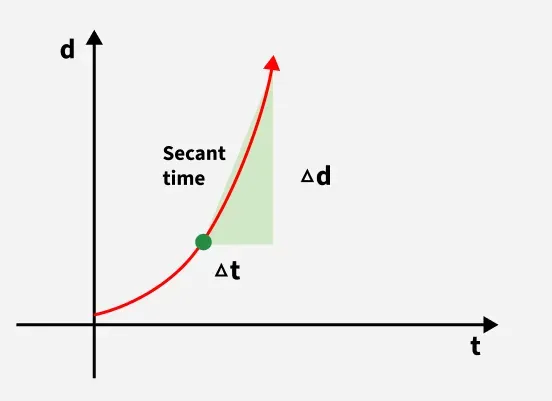 Average velocity in a distance-time graph
Average velocity in a distance-time graphDifference Between Average Speed and Average Velocity
- Average speed and average velocity are both measures of motion, but they are distinct in how they are calculated and interpreted.
- Average speed is a scalar quantity that refers to the total distance traveled divided by the total time taken, regardless of the direction of motion. It gives an overall measure of how fast an object is moving, without considering the path taken.
- On the other hand, average velocity is a vector quantity, which means it also takes direction into account. It is calculated by dividing the total displacement (the straight-line distance between the starting and ending points) by the total time elapsed. Average velocity provides information not only about the speed but also about the direction of motion.
- In short, while average speed measures the total distance covered, average velocity measures how far an object has moved in a specific direction over a given period of time.
Solved Examples
Question 1. Find the average velocity between t = 1 and t = 4, for the particle which is moving in a plane and whose position is: r = ti + tj.
Given: the initial and final position vectors,
r = ti + tj
The position vector changes with time. The average velocity is given by the formula,
\vec{v} = \frac{\vec{r} - \vec{r'}}{\Delta t}
At t = 1
r = 1i + 1j
At t = 4
r' = 4i + 4j
\Delta t = 3
Plugging the values in this above equation,
\vec{v} = \frac{\vec{r'} - \vec{r}}{\Delta t}\\ = \vec{v} = \frac{4\hat{i} + 4\hat{j} - (\hat{i} + \hat{j})}{3} \\ = \vec{v} = \frac{3\hat{i} + 3\hat{j}}{3}
→vavg= 1i^+1j^
Question 2: Find the displacement vector for the particle which is moving in a plane and whose position vectors are : vi = 3i + 4j and vf = 5i + 2j
Given: the initial and final position vectors,
vi = 3i + 4j
vf = 5i + 2j
The goal is find the displacement vector 'd ' It is given by,
Δd=vf −vi
Plugging the values in this above equation,
d=(5i^+2j^)−(3i^+4j^)
d=(5−3)i^+(2−4)j^
d=2i^−2j^
The displacement vector of the particle is:
d=2i^−2j^
Question 3: Find the displacement vector for the particle which is moving in a plane and whose position vectors are, vi = i + j and vf = 2i + 5j
Given: the initial and final position vectors,
vi = i + j
vf = 2i + 5j
The goal is to find the displacement vector d. It is given by,
Δd=vf −vi
d=(2i^+5j^)−(i^+j^)
d=(2−1)i^+(5−1)j^
d=1i^+ 4j^
The displacement vector of the particle is:
d=i^+4j^
Question 4: Find the velocity at t = 4, for the particle which is moving in a plane and whose position is given: r = 2t2i + t3j
Given: the initial and final position vectors,
r = 2t2i + t3j
We need to find the velocity at t=4.
The velocity vector is the derivative of the position vector with respect to time,
v=dr/dt
So, let's differentiate the given position vector r=2t2i + t3j with respect to time:
Differentiate with respect to t,
d/dt (2t2i^) =4ti^
So the velocity vector is:
v=4ti^+3t2j^
Plugging the values in this above equation,
v=4(4)i^+3(4)2j^
v=16i^+48j^
Question 5: Find the velocity at t = 2, for the particle which is moving in a plane and whose position is given :r = ti + 4t2j
Given: the initial and final position vectors,
r = ti + 4t2j
The velocity vector is the derivative of the position vector with respect to time,
v=dr/dt
So, let's differentiate the given position vector r=ti^+4t2j^with respect to time:
Differentiate with respect to t,
d/dt (ti^) =1i^
So the velocity vector is:
v=1i^+8tj^
Plugging the values in this above equation,
v=1i^+16j^
Question 6: Find the average velocity between t = 0 and t = 2, for the particle which is moving in a plane and whose position is given : r = 3ti + 3t3j
Given: the initial and final position vectors,
r = 3ti + 3t3j
The position vector: r(t)=3ti^+3t3j^
The average velocity between t=t1 and t=t2 is given by the formula,
vavg=r(t2)−r(t1)/t2-t1
Find r(t1) at t=0:
r(0)=3(0)i^+3(0)3j^=0i^+0j^=0
Find r(t2) at t=2:
r(2)=3(2)i^+3(2)3j^=6i^+3(8)j^= 6i^+24j^
Plugging the values in this above equation,
vavg= r(2)-r(0)/2-0
vavg= (6i^+24j^)−(0i^+0j^)/2
vavg=6i^+24j^/2
vavg=3i^+12j^
Related Reads,