Automating some git commands with Python
Last Updated : 28 Apr, 2025
Git is a powerful version control system that developers widely use to manage their code. However, managing Git repositories can be a tedious task, especially when working with multiple branches and commits. Fortunately, Git's command-line interface can be automated using Python, making it easier to manage your code and automate common tasks.
One popular library for automating Git commands with Python is GitPython. It provides an easy-to-use interface for interacting with Git repositories, allowing you to perform tasks such as creating branches, committing changes, and merging branches.
To start automating Git commands with Python, you will first need to install GitPython by running the following command:
pip install GitPython
Automate Git Commands with Python
1. Initialize and open a local repository
- To initialize a new repository
Python3 from git import Repo new_repo = Repo.init('/path/to/new/repo_directory') - To Open the Existing local repository
Python3 from git import Repo existing_repo = Repo('path/to/existing/repo') 2. Clone a remote Repository
To create a local copy of the repository at the specified local_path directory, using the repository URL repo_url
import git repo = gitRepo.clone_from('https://github.com/username/repository', '/path/to/local/directory') Example:
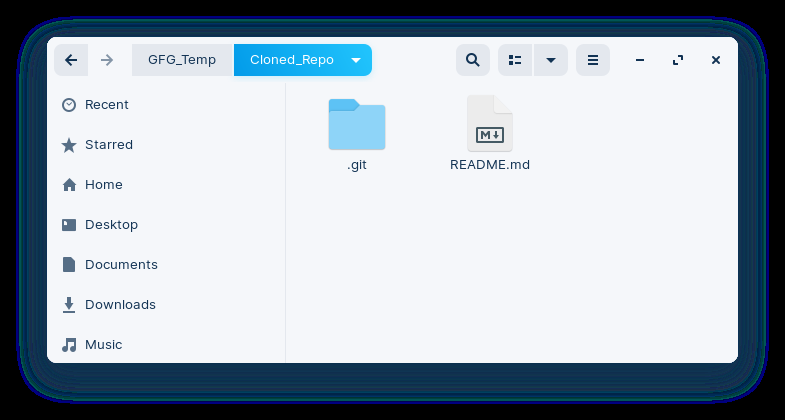
Python3 import git # Clone a remote repository repo_url = "https://github.com/Hardik-Kushwaha/GIT_Python_Automation" local_path = "/home/hardik/GFG_Temp/Cloned_Repo" repo = git.Repo.clone_from(repo_url, local_path) print(f'Repository Cloned at location: {local_path}') Output:
Repository Cloned at location: /home/hardik/GFG_Temp/Cloned_Repo
Verify: Go to the location where you cloned the repository to verify it.
3. Add and Commit files
Add Files: Add the specified files to the index, preparing them to be committed.
repo.index.add(['file1', 'file2'])
Add Commit: Create a new commit in the local repository with the specified commit message.
repo.index.commit('Your Commit Message') Example:
Python3 import git repo = git.Repo('/home/hardik/GFG_Temp/Cloned_Repo') # Do some changes and commit file1 = 'test-sample.jpg' file2 = 'input.txt' repo.index.add([file1,file2]) print('Files Added Successfully') repo.index.commit('Initial commit on new branch') print('Commited successfully') Output:
Files Added Successfully Commited successfully

4. Push to a remote Repository
Push the local commits to the remote repository
origin = repo.remote(name='origin') origin.push()
Example:
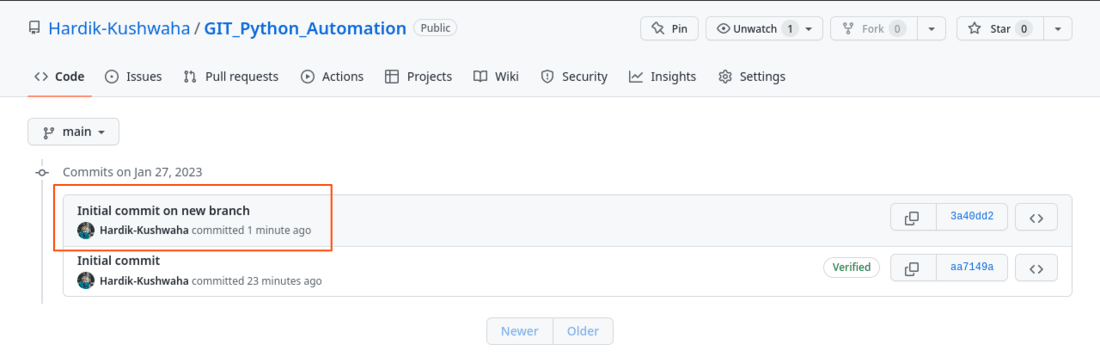
Python3 import git repo = git.Repo("/home/hardik/GFG_Temp/Cloned_Repo") origin = repo.remote(name='origin') existing_branch = repo.heads['main'] existing_branch.checkout() repo.index.commit('Initial commit on new branch') print('Commited successfully') origin.push() print('Pushed changes to origin') Output:
Commited successfully Pushed changes to origin
Verify:
5. Create a new branch
To create a new branch, you can use the create_head() method of the Repo class, which creates a new branch with the specified name
new_branch = repo.create_head('new_branch') To checkout the new branch
new_branch.checkout()
Example:
Python3 import git # Initialize a new repository repo = git.Repo.init('/home/hardik/GFG_Temp/Cloned_Repo') # Create a new branch new_branch = repo.create_head('new_branch') print('New Branch Created') # Checkout the new branch new_branch.checkout() print("Changed the current branch to new_branch") Output:
In this example, we first initialize a new repository using git.Repo.init() method. We then create a new branch called new_branch using the create_head() method. We then check out the new branch using the checkout() method.
New Branch Created Changed the current branch to new_branch
To switch to an existing branch, you can use the heads attribute of the Repo class, which returns a list of branches, and then call the checkout method on the desired branch.
Python3 import git repo = git.Repo('/home/hardik/GFG_Temp/Cloned_Repo') # Select an existing branch existing_branch = repo.heads['existing_branch'] existing_branch.checkout() print('Branch Changed to an existing branch') Output:
Branch Changed to an existing branch
6. Pull from a remote repository
To update the local repository with the latest changes from the remote repository we use git pull command
Example:
Python3 import git repo = git.Repo("/path/to/local/repo") origin = repo.remote(name='origin') origin.pull() Output:
Pulled Changes from the origin
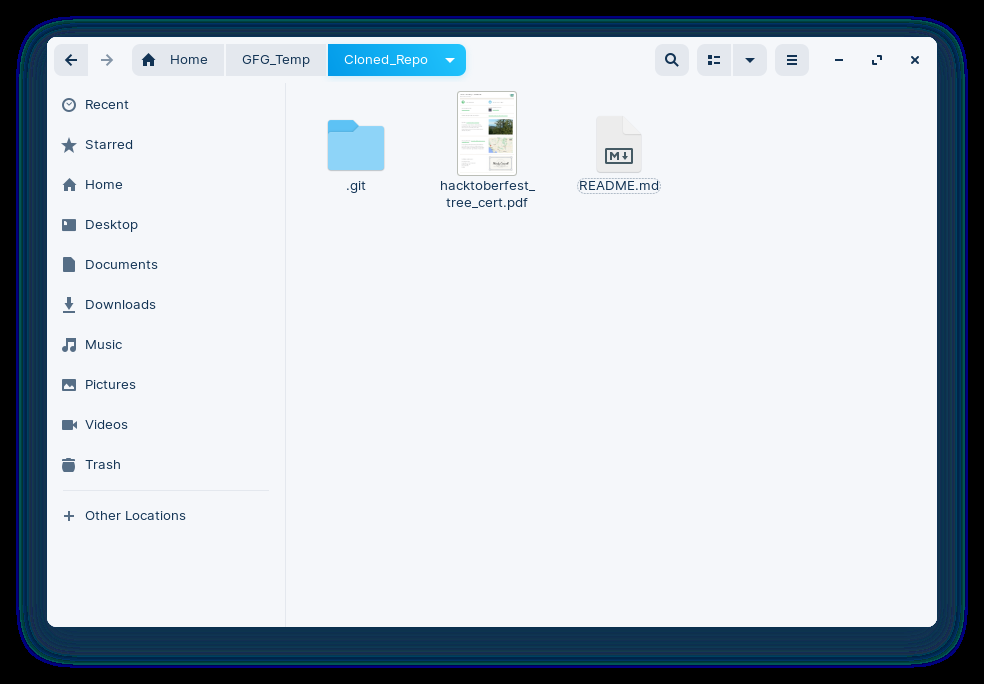
Verify: New file hacktoberfest_tree_cert.pdf got pulled from the origin and got saved to the local machine.
Similar Reads
Executing Shell Commands with Python This article starts with a basic introduction to Python shell commands and why one should use them. It also describes the three primary ways to run Python shell commands.os.system()subprocess.run()subprocess.Popen()Â What is a shell in the os?In programming, the shell is a software interface for acce
4 min read
Automated SSH bot in Python In this article, we are going to see how we can use Python to Automate some basic SSH processes. What is SSH? SSH stands for Secure Shell or Secure Socket Shell, in simple terms, it is a network communication protocol used to communicate between two computers and share data among them. The main feat
8 min read
Python | Set 6 (Command Line and Variable Arguments) Previous Python Articles (Set 1 | Set 2 | Set 3 | Set 4 | Set 5) This article is focused on command line arguments as well as variable arguments (args and kwargs) for the functions in python. Command Line Arguments Till now, we have taken input in python using raw_input() or input() [for integers].
2 min read
How to Use Git Shell Commands? Git is a powerful version control system that is important for managing source code in modern software development. While there are many graphical user interfaces (GUIs) available for Git, mastering Git shell commands can significantly enhance your productivity and control over your repositories. Th
3 min read
Customizing Git Hooks for Workflow Automation Git is a distributed version control system that monitors changes to a project. Git hooks are scripts that run in response to Git events such as commit or push. They automate tasks, enforce rules, and can be tailored to your project's requirements. A pre-commit hook, for example, can detect errors i
7 min read